LET-418/Mi2 and SPR-5/LSD1 cooperatively prevent somatic reprogramming of C. elegans germline stem cells
- PMID: 24749077
- PMCID: PMC3986580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.02.007
LET-418/Mi2 and SPR-5/LSD1 cooperatively prevent somatic reprogramming of C. elegans germline stem cells
Abstract
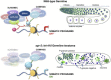
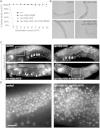
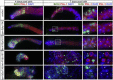
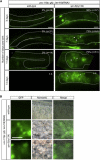
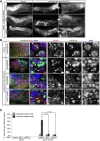
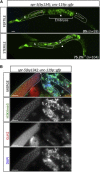
Throughout their journey to forming new individuals, germline stem cells must remain totipotent, particularly by maintaining a specific chromatin structure. However, the place epigenetic factors occupy in this process remains elusive. So far, "sensitization" of chromatin by modulation of histone arrangement and/or content was believed to facilitate transcription-factor-induced germ cell reprogramming. Here, we demonstrate that the combined reduction of two epigenetic factors suffices to reprogram C. elegans germ cells. The histone H3K4 demethylase SPR-5/LSD1 and the chromatin remodeler LET-418/Mi2 function together in an early process to maintain germ cell status and act as a barrier to block precocious differentiation. This epigenetic barrier is capable of limiting COMPASS-mediated H3K4 methylation, because elevated H3K4me3 levels correlate with germ cell reprogramming in spr-5; let-418 mutants. Interestingly, germ cells deficient for spr-5 and let-418 mainly reprogram as neurons, suggesting that neuronal fate might be the first to be derepressed in early embryogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Adamo A., Sesé B., Boue S., Castaño J., Paramonov I., Barrero M.J., Izpisua Belmonte J.C. LSD1 regulates the balance between self-renewal and differentiation in human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011;13:652–659. - PubMed
-
- Belfiore M., Pugnale P., Saudan Z., Puoti A. Roles of the C. elegans cyclophilin-like protein MOG-6 in MEP-1 binding and germline fates. Development. 2004;131:2935–2945. - PubMed
-
- Biedermann B., Wright J., Senften M., Kalchhauser I., Sarathy G., Lee M.H., Ciosk R. Translational repression of cyclin E prevents precocious mitosis and embryonic gene activation during C. elegans meiosis. Dev. Cell. 2009;17:355–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

