Prize-based contingency management for the treatment of substance abusers: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24750232
- PMCID: PMC4203362
- DOI: 10.1111/add.12589
Prize-based contingency management for the treatment of substance abusers: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To review randomized controlled trials to assess efficacy of a prize-based contingency management procedure in reducing substance use (where a drug-free breath or urine sample provides a chance of winning a prize).
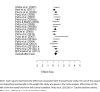
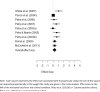
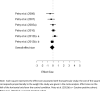
Methods: A meta-analysis was conducted on papers published from January 2000 to February 2013 to determine the effect size of studies comparing prize-based contingency management to a treatment-as-usual control condition (k = 19 studies). Parallel analyses evaluated the efficacy of both short- (k = nine studies) and long-term outcomes (k = six studies) of prize-based contingency management.
Results: The average end-of-treatment effect size (Cohen's d) was 0.46 [95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.37, 0.54]. This effect size decreased at the short-term (≤3-month) post-intervention follow-up to 0.33 (95% CI = 0.12, 0.54) and at the 6-month follow-up time-point there was no detectable effect [d = -0.09 (95% CI = -0.28, 0.10)].
Conclusion: Adding prize-based contingency management to behavioral support for substance use disorders can increase short-term abstinence, but the effect does not appear to persist to 6 months.
Keywords: Contingency management; incentives; meta-analysis; prize-based; substance abuse treatment; substance use disorder.
© 2014 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
References
-
- Bigelow G, Silverman K. Theoretical and empirical foundations of contingency management treatments for drug abuse. In: Higgins ST, Silverman K, editors. Motivating behavior change among illicit-drug abusers: Research on contingency management interventions. American Psychological Association; Washington, DC: 1999.
-
- Petry NM, Stitzer ML. Contingency management: Using motivational incentives to improve drug abuse treatment. Yale University Psychotherapy Development Center; West Haven, CT: 2002.
-
- Bigelow GE, Stitzer ML, Griffiths RR, Liebson IA. Contingency management approaches to drug self-administration and drug abuse: Efficacy and limitations. Addict Behav. 1981;6:241–252. - PubMed
-
- Higgins ST, Alessi SM, Dantona RL. Voucher-based incentives: A substance abuse treatment innovation. Addict Behav. 2002;27:887–910. - PubMed
-
- Higgins ST, Heil SH, Lussier JP. Clinical implications of reinforcement as a determinant of substance use disorders. Annu Rev Psychol. 2004;55:431–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical