Molecular characterization of cryptically circulating rabies virus from ferret badgers, Taiwan
- PMID: 24751120
- PMCID: PMC4012806
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2005.131389
Molecular characterization of cryptically circulating rabies virus from ferret badgers, Taiwan
Abstract
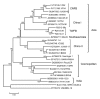
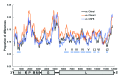
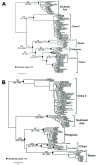
After the last reported cases of rabies in a human in 1959 and a nonhuman animal in 1961, Taiwan was considered free from rabies. However, during 2012-2013, an outbreak occurred among ferret badgers in Taiwan. To examine the origin of this virus strain, we sequenced 3 complete genomes and acquired multiple rabies virus (RABV) nucleoprotein and glycoprotein sequences. Phylogeographic analyses demonstrated that the RABV affecting the Taiwan ferret badgers (RABV-TWFB) is a distinct lineage within the group of lineages from Asia and that it has been differentiated from its closest lineages, China I (including isolates from Chinese ferret badgers) and the Philippines, 158-210 years ago. The most recent common ancestor of RABV-TWFB originated 91-113 years ago. Our findings indicate that RABV could be cryptically circulating in the environment. An understanding of the underlying mechanism might shed light on the complex interaction between RABV and its host.
Keywords: Melogale moschata subaurantiaca; Rabies; Taiwan; ferret badger; origin; phylogeography; viruses.
Figures


References
-
- Jackson AC. Pathogenesis. In: Jackson AC, Wunner WH, editors. Rabies. London: Elsevier Academic Press; 2007.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies: second report. Geneva. Organization. 2013;•••:1–139. - PubMed
-
- Wandeler A. Virus infections of non-domestic carnivores: rabies virus. In: Appel MJ, editor. Virus infections of carnivores. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers; 1987. p. 449–61.
-
- Barnard BJH. The role played by wildlife in the epizootiology of rabies in South Africa and South-West Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1979;46:155–63 . - PubMed
-
- Smith GC, Wilkinson D. Modelling disease spread in a novel host: rabies in the European badger Meles meles. J Appl Ecol. 2002;39:865–74. 10.1046/j.1365-2664.2002.00773.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

