Patellins 3 and 6, two members of the Plant Patellin family, interact with the movement protein of Alfalfa mosaic virus and interfere with viral movement
- PMID: 24751128
- PMCID: PMC6638666
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12146
Patellins 3 and 6, two members of the Plant Patellin family, interact with the movement protein of Alfalfa mosaic virus and interfere with viral movement
Abstract
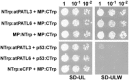
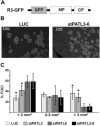
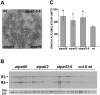
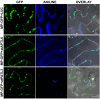
Movement proteins (MPs) encoded by plant viruses interact with host proteins to facilitate or interfere with intra- and/or intercellular viral movement. Using yeast two-hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays, we herein present in vivo evidence for the interaction between Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV) MP and Arabidopsis Patellin 3 (atPATL3) and Patellin 6 (atPATL6), two proteins containing a Sec14 domain. Proteins with Sec14 domains are implicated in membrane trafficking, cytoskeleton dynamics, lipid metabolism and lipid-mediated regulatory functions. Interestingly, the overexpression of atPATL3 and/or atPATL6 interfered with the plasmodesmata targeting of AMV MP and correlated with reduced infection foci size. Consistently, the viral RNA levels increased in the single and double Arabidopsis knockout mutants for atPATL3 and atPATL6. Our results indicate that, in general, MP-PATL interactions interfere with the correct subcellular targeting of MP, thus rendering the intracellular transport of viral MP-containing complexes less efficient and diminishing cell-to-cell movement.
Keywords: AMV; ilarvirus; intercellular movement; movement protein; patellin.
© 2014 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures


References
-
- Allen‐Baume, V. , Segui, B. and Cockcroft, S. (2002) Current thoughts on the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein family. FEBS Lett. 531, 74–80. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, F. , Sánchez‐Navarro, J.A. and Pallas, V. (2006) In vitro and in vivo mapping of the Prunus necrotic ringspot virus coat protein C‐terminal dimerization domain by bimolecular fluorescence complementation. J. Gen. Virol. 87, 1745–1750. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, F. , Sánchez‐Navarro, J.A. and Pallas, V. (2010) Implication of the C terminus of the Prunus necrotic ringspot virus movement protein in cell‐to‐cell transport and in its interaction with the coat protein. J. Gen. Virol. 91, 1865–1870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

