Hepatic HMOX1 expression positively correlates with Bach-1 and miR-122 in patients with HCV mono and HIV/HCV coinfection
- PMID: 24752012
- PMCID: PMC3994072
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095564
Hepatic HMOX1 expression positively correlates with Bach-1 and miR-122 in patients with HCV mono and HIV/HCV coinfection
Abstract
Aim: To analyze the expression of HMOX1 and miR-122 in liver biopsy samples obtained from HCV mono-and HIV/HCV co-infected patients in relation to selected clinical parameters, histological examination and IL-28B polymorphism as well as to determine whether HMOX1 expression is dependent on Bach-1.
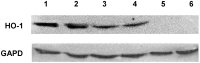
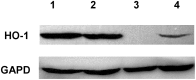
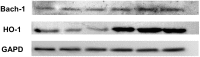
Materials and methods: The study group consisted of 90 patients with CHC: 69 with HCV mono and 21 with HIV/HCV co-infection. RT-PCR was used in the analysis of HMOX1, Bach-1 and miR-122 expression in liver biopsy samples and in the assessment of IL-28B single-nucleotide polymorphism C/T (rs12979860) in the blood. Moreover in liver biopsy samples an analysis of HO-1 and Bach-1 protein level by Western Blot was performed.
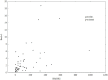
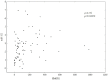
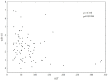
Results: HCV mono-infected patients, with lower grading score (G<2) and higher HCV viral load (>600000 IU/mL) demonstrated higher expression of HMOX1. In patients with HIV/HCV co-infection, the expression of HMOX1 was lower in patients with lower lymphocyte CD4 count and higher HIV viral load. IL28B polymorphism did not affect the expression of either HMOX1 or miR-122. Higher HMOX1 expression correlated with higher expression of Bach-1 (Spearman's ρ = 0.586, p = 0.000001) and miR-122 (Spearman's ρ = 0.270, p = 0.014059).
Conclusions: HMOX1 and miR-122 play an important role in the pathogenesis of CHC in HCV mono-and HIV/HCV co-infected patients. Reduced expression of HMOX1 in patients with HIV/HCV co-infection may indicate a worse prognosis in this group. Our results do not support the importance of Bach-1 in repression of HMOX1 in patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lauer GM, Walker BD (2001) Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 345: 41–52. - PubMed
-
- Caballeria L, Pares A, Castells A, Gines A, Bru C, et al. (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma in primary biliary cirrhosis: similar incidence to that in hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 96: 1160–1163. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson IM, McHutchison JG, Dusheiko G, Di Bisceglie AM, Reddy KR, et al. (2011) Telaprevir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 364: 2405–2416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

