MicroRNA-519a is a novel oncomir conferring tamoxifen resistance by targeting a network of tumour-suppressor genes in ER+ breast cancer
- PMID: 24752803
- PMCID: PMC4298809
- DOI: 10.1002/path.4363
MicroRNA-519a is a novel oncomir conferring tamoxifen resistance by targeting a network of tumour-suppressor genes in ER+ breast cancer
Abstract
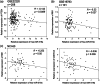
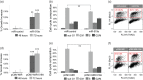
Tamoxifen is an endocrine therapy which is administered to up to 70% of all breast cancer patients with oestrogen receptor alpha (ERα) expression. Despite the initial response, most patients eventually acquire resistance to the drug. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNAs which have the ability to post-transcriptionally regulate genes. Although the role of a few miRNAs has been described in tamoxifen resistance at the single gene/target level, little is known about how concerted actions of miRNAs targeting biological networks contribute to resistance. Here we identified the miRNA cluster, C19MC, which harbours around 50 mature miRNAs, to be up-regulated in resistant cells, with miRNA-519a being the most highly up-regulated. We could demonstrate that miRNA-519a regulates tamoxifen resistance using gain- and loss-of-function testing. By combining functional enrichment analysis and prediction algorithms, we identified three central tumour-suppressor genes (TSGs) in PI3K signalling and the cell cycle network as direct target genes of miR-519a. Combined expression of these target genes correlated with disease-specific survival in a cohort of tamoxifen-treated patients. We identified miRNA-519a as a novel oncomir in ER+ breast cancer cells as it increased cell viability and cell cycle progression as well as resistance to tamoxifen-induced apoptosis. Finally, we could show that elevated miRNA-519a levels were inversely correlated with the target genes' expression and that higher expression of this miRNA correlated with poorer survival in ER+ breast cancer patients. Hence we have identified miRNA-519a as a novel oncomir, co-regulating a network of TSGs in breast cancer and conferring resistance to tamoxifen. Using inhibitors of such miRNAs may serve as a novel therapeutic approach to combat resistance to therapy as well as proliferation and evasion of apoptosis in breast cancer.
Keywords: C19MC cluster; breast cancer; cell cycle network; microRNAs; tamoxifen resistance.
© 2014 The Authors. The Journal of Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures






References
-
- Vargo-Gogola T, Rosen JM. Modelling breast cancer: one size does not fit all. Nature Rev Cancer. 2007;7:659–672. - PubMed
-
- Jordan VC, Murphy CS. Endocrine pharmacology of antiestrogens as antitumor agents. Endocr Rev. 1990;11:578–610. - PubMed
-
- Katzenellenbogen BS, Miller MA, Mullick A, et al. Antiestrogen action in breast cancer cells: modulation of proliferation and protein synthesis, and interaction with estrogen receptors and additional antiestrogen binding sites. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1985;5:231–243. - PubMed
-
- Ring A, Dowsett M. Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004;11:643–658. - PubMed
-
- Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, et al. The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell. 1998;95:927–937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

