Novel domains of expression for orphan receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 in the human and mouse reproductive system
- PMID: 24753105
- PMCID: PMC4258601
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24138
Novel domains of expression for orphan receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 in the human and mouse reproductive system
Abstract
Background: The noncanonical Wnt receptor and tyrosine kinase Ror2 has been associated with recessive Robinow syndrome (RRS) and dominant brachydactyly type B1. The phenotypes of mouse mutants implicate Ror2 in the development of the heart, lungs, bone, and craniofacial structures, which are affected in RRS. Following a recently identified role of Ror2 in the migration of mouse primordial germ cells, we extensively characterized its expression throughout the fetal internal reproductive system and the postnatal ductal system.
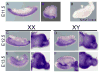
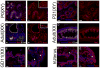
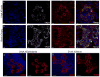
Results: We show that Ror2 gene products are present in the germ cells and somatic cells of the testis and the ovary of both the mouse and human fetus. In reproductive tract structures, we find that Ror2 is expressed in the mesonephros, developing Wolffian and Müllerian ducts, and later in their derivatives, the epididymal epithelium and uterine epithelium.
Conclusions: This study sets the stage to explore function for this tyrosine kinase receptor in novel regions of expression in the developing reproductive system in both mouse and human.
Keywords: Müllerian duct; Ror2; Sertoli cell; Wnt5a; Wolffian duct; germ cell; granulosa cell; ovary; testis.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Diagnostic evaluation of the infertile female: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2012a;98:302–307. - PubMed
-
- Diagnostic evaluation of the infertile male: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2012b;98:294–301. - PubMed
-
- Afzal AR, Jeffery S. One gene, two phenotypes: ROR2 mutations in autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome and autosomal dominant brachydactyly type B. Hum Mutat. 2003;22:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Afzal AR, Rajab A, Fenske CD, Oldridge M, Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E, Tuysuz B, Murday VA, Patton MA, Wilkie AO, Jeffery S. Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat Genet. 2000;25:419–422. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shawi R, Ashton SV, Underwood C, Simons JP. Expression of the Ror1 and Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase genes during mouse development. Dev Genes Evol. 2001;211:161–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

