An outer membrane channel protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with exotoxin activity
- PMID: 24753609
- PMCID: PMC4020113
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1400136111
An outer membrane channel protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with exotoxin activity
Abstract
The ability to control the timing and mode of host cell death plays a pivotal role in microbial infections. Many bacteria use toxins to kill host cells and evade immune responses. Such toxins are unknown in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Virulent M. tuberculosis strains induce necrotic cell death in macrophages by an obscure molecular mechanism. Here we show that the M. tuberculosis protein Rv3903c (channel protein with necrosis-inducing toxin, CpnT) consists of an N-terminal channel domain that is used for uptake of nutrients across the outer membrane and a secreted toxic C-terminal domain. Infection experiments revealed that CpnT is required for survival and cytotoxicity of M. tuberculosis in macrophages. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the C-terminal domain of CpnT causes necrotic cell death in eukaryotic cells. Thus, CpnT has a dual function in uptake of nutrients and induction of host cell death by M. tuberculosis.
Keywords: pore; secretion; transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
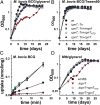

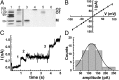
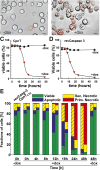
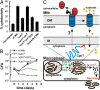
References
-
- Collier RJ. Understanding the mode of action of diphtheria toxin: A perspective on progress during the 20th century. Toxicon. 2001;39(11):1793–1803. - PubMed
-
- Gordon SV, Bottai D, Simeone R, Stinear TP, Brosch R. Pathogenicity in the tubercle bacillus: Molecular and evolutionary determinants. Bioessays. 2009;31(4):378–388. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay S, Nair S, Ghosh S. Pathogenesis in tuberculosis: Transcriptomic approaches to unraveling virulence mechanisms and finding new drug targets. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012;36(2):463–485. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization 2013. Global Tuberculosis Control, WHO report 2012 (World Health Organization)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

