Discovery and characterization of a G protein-biased agonist that inhibits β-arrestin recruitment to the D2 dopamine receptor
- PMID: 24755247
- PMCID: PMC4054005
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.113.090563
Discovery and characterization of a G protein-biased agonist that inhibits β-arrestin recruitment to the D2 dopamine receptor
Abstract
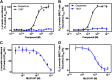
A high-throughput screening campaign was conducted to interrogate a 380,000+ small-molecule library for novel D2 dopamine receptor modulators using a calcium mobilization assay. Active agonist compounds from the primary screen were examined for orthogonal D2 dopamine receptor signaling activities including cAMP modulation and β-arrestin recruitment. Although the majority of the subsequently confirmed hits activated all signaling pathways tested, several compounds showed a diminished ability to stimulate β-arrestin recruitment. One such compound (MLS1547; 5-chloro-7-[(4-pyridin-2-ylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]quinolin-8-ol) is a highly efficacious agonist at D2 receptor-mediated G protein-linked signaling, but does not recruit β-arrestin as demonstrated using two different assays. This compound does, however, antagonize dopamine-stimulated β-arrestin recruitment to the D2 receptor. In an effort to investigate the chemical scaffold of MLS1547 further, we characterized a set of 24 analogs of MLS1547 with respect to their ability to inhibit cAMP accumulation or stimulate β-arrestin recruitment. A number of the analogs were similar to MLS1547 in that they displayed agonist activity for inhibiting cAMP accumulation, but did not stimulate β-arrestin recruitment (i.e., they were highly biased). In contrast, other analogs displayed various degrees of G protein signaling bias. These results provided the basis to use pharmacophore modeling and molecular docking analyses to build a preliminary structure-activity relationship of the functionally selective properties of this series of compounds. In summary, we have identified and characterized a novel G protein-biased agonist of the D2 dopamine receptor and identified structural features that may contribute to its biased signaling properties.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures



References
-
- Banala AK, Levy BA, Khatri SS, Furman CA, Roof RA, Mishra Y, Griffin SA, Sibley DR, Luedtke RR, Newman AH. (2011) N-(3-fluoro-4-(4-(2-methoxy or 2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazine-1-yl)butyl)arylcarboxamides as selective dopamine D3 receptor ligands: critical role of the carboxamide linker for D3 receptor selectivity. J Med Chem 54:3581–3594 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baum B, Mohamed M, Zayed M, Gerlach C, Heine A, Hangauer D, Klebe G. (2009) More than a simple lipophilic contact: a detailed thermodynamic analysis of nonbasic residues in the s1 pocket of thrombin. J Mol Biol 390:56–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

