Heparan sulfate signaling in cancer
- PMID: 24755488
- PMCID: PMC4065786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.03.001
Heparan sulfate signaling in cancer
Abstract
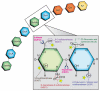
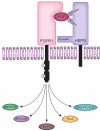
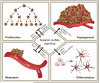
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a biopolymer consisting of variably sulfated repeating disaccharide units. The anticoagulant heparin is a highly sulfated intracellular variant of HS. HS has demonstrated roles in embryonic development, homeostasis, and human disease via non-covalent interactions with numerous cellular proteins, including growth factors and their receptors. HS can function as a co-receptor by enhancing receptor-complex formation. In other contexts, HS disrupts signaling complexes or serves as a ligand sink. The effects of HS on growth factor signaling are tightly regulated by the actions of sulfyltransferases, sulfatases, and heparanases. HS has important emerging roles in oncogenesis, and heparin derivatives represent potential therapeutic strategies for human cancers. Here we review recent insights into HS signaling in tumor proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, and differentiation. A cancer-specific understanding of HS signaling could uncover potential therapeutic targets in this highly actionable signaling network.
Keywords: heparan sulfate; heparanase; heparin; metastasis; sulfatase; sulfyltransferase.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactions of signaling proteins, growth factors and other proteins with heparan sulfate: mechanisms and mysteries.Connect Tissue Res. 2015;56(4):272-80. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2015.1045066. Connect Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 26076122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparan Sulfate Mimetics in Cancer Therapy: The Challenge to Define Structural Determinants and the Relevance of Targets for Optimal Activity.Molecules. 2018 Nov 8;23(11):2915. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112915. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30413079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparan sulfate S-domains and extracellular sulfatases (Sulfs): their possible roles in protein aggregation diseases.Glycoconj J. 2018 Aug;35(4):387-396. doi: 10.1007/s10719-018-9833-8. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Glycoconj J. 2018. PMID: 30003471 Review.
-
Heparanase: Historical Aspects and Future Perspectives.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1221:71-96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34521-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32274707 Review.
-
Transgenic or tumor-induced expression of heparanase upregulates sulfation of heparan sulfate.Nat Chem Biol. 2007 Dec;3(12):773-8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.41. Epub 2007 Oct 21. Nat Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17952066
Cited by
-
The Role of Proteoglycans in Cancer Metastasis and Circulating Tumor Cell Analysis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 26;8:749. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00749. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32984308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparanase modulation by Wingless/INT (Wnt).Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Apr;48(4):3117-3125. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06348-3. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33891270
-
Glycosaminoglycan-Protein Interactions and Their Roles in Human Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 9;8:639666. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.639666. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33768117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Peritumoural Brain Zone of Glioblastoma: CDK4 and EXT2 May Be Potential Drivers of Malignancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2835. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032835. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769158 Free PMC article.
-
CTGF/VEGFA-activated Fibroblasts Promote Tumor Migration Through Micro-environmental Modulation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 Aug;17(8):1502-1514. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000708. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29669735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howell WH, Holt E. Two new factors in blood coagulation-heparin and pro-antithrombin. American Journal of Physiology. 1918;47:328–341.
-
- Linker A, et al. Heparitin sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958;29:443–444. - PubMed
-
- Olson ST, Shore JD. Binding of high affinity heparin to antithrombin III. Characterization of the protein fluorescence enhancement. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:11065–11072. - PubMed
-
- Rabenstein DL. Heparin and heparan sulfate: structure and function. Natural product reports. 2002;19:312–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

