Contrasting Roles of the Apoplastic Aspartyl Protease APOPLASTIC, ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1-DEPENDENT1 and LEGUME LECTIN-LIKE PROTEIN1 in Arabidopsis Systemic Acquired Resistance
- PMID: 24755512
- PMCID: PMC4044859
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.239665
Contrasting Roles of the Apoplastic Aspartyl Protease APOPLASTIC, ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1-DEPENDENT1 and LEGUME LECTIN-LIKE PROTEIN1 in Arabidopsis Systemic Acquired Resistance
Abstract
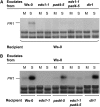
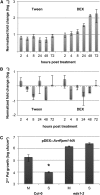
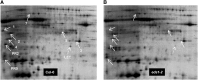
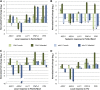
Systemic acquired resistance (SAR) is an inducible immune response that depends on ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 (EDS1). Here, we show that Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) EDS1 is required for both SAR signal generation in primary infected leaves and SAR signal perception in systemic uninfected tissues. In contrast to SAR signal generation, local resistance remains intact in eds1 mutant plants in response to Pseudomonas syringae delivering the effector protein AvrRpm1. We utilized the SAR-specific phenotype of the eds1 mutant to identify new SAR regulatory proteins in plants conditionally expressing AvrRpm1. Comparative proteomic analysis of apoplast-enriched extracts from AvrRpm1-expressing wild-type and eds1 mutant plants led to the identification of 12 APOPLASTIC, EDS1-DEPENDENT (AED) proteins. The genes encoding AED1, a predicted aspartyl protease, and another AED, LEGUME LECTIN-LIKE PROTEIN1 (LLP1), were induced locally and systemically during SAR signaling and locally by salicylic acid (SA) or its functional analog, benzo 1,2,3-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester. Because conditional overaccumulation of AED1-hemagglutinin inhibited SA-induced resistance and SAR but not local resistance, the data suggest that AED1 is part of a homeostatic feedback mechanism regulating systemic immunity. In llp1 mutant plants, SAR was compromised, whereas the local resistance that is normally associated with EDS1 and SA as well as responses to exogenous SA appeared largely unaffected. Together, these data indicate that LLP1 promotes systemic rather than local immunity, possibly in parallel with SA. Our analysis reveals new positive and negative components of SAR and reinforces the notion that SAR represents a distinct phase of plant immunity beyond local resistance.
© 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akoh CC, Lee GC, Liaw YC, Huang TH, Shaw JF. (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43: 534–552 - PubMed
-
- Armijo G, Salinas P, Monteoliva MI, Seguel A, García C, Villarroel-Candia E, Song W, van der Krol AR, Álvarez ME, Holuigue L. (2013) A salicylic acid-induced lectin-like protein plays a positive role in the effector-triggered immunity response of Arabidopsis thaliana to Pseudomonas syringae Avr-Rpm1. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26: 1395–1406 - PubMed
-
- Bartsch M, Gobbato E, Bednarek P, Debey S, Schultze JL, Bautor J, Parker JE. (2006) Salicylic acid-independent ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 signaling in Arabidopsis immunity and cell death is regulated by the monooxygenase FMO1 and the Nudix hydrolase NUDT7. Plant Cell 18: 1038–1051 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

