Hacking on decoy-state quantum key distribution system with partial phase randomization
- PMID: 24755767
- PMCID: PMC3996487
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04759
Hacking on decoy-state quantum key distribution system with partial phase randomization
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Hacking on decoy-state quantum key distribution system with partial phase randomization.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 9;8:46943. doi: 10.1038/srep46943. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29424374 Free PMC article.
Abstract
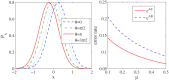
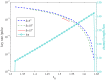
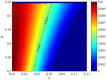
Quantum key distribution (QKD) provides means for unconditional secure key transmission between two distant parties. However, in practical implementations, it suffers from quantum hacking due to device imperfections. Here we propose a hybrid measurement attack, with only linear optics, homodyne detection, and single photon detection, to the widely used vacuum + weak decoy state QKD system when the phase of source is partially randomized. Our analysis shows that, in some parameter regimes, the proposed attack would result in an entanglement breaking channel but still be able to trick the legitimate users to believe they have transmitted secure keys. That is, the eavesdropper is able to steal all the key information without discovered by the users. Thus, our proposal reveals that partial phase randomization is not sufficient to guarantee the security of phase-encoding QKD systems with weak coherent states.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantum man-in-the-middle attack on the calibration process of quantum key distribution.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 9;8(1):4283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22700-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29523828 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting a Photon-Number Splitting Attack in Decoy-State Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution via Statistical Hypothesis Testing.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;24(9):1232. doi: 10.3390/e24091232. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36141118 Free PMC article.
-
Long-distance measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with coherent-state superpositions.Opt Lett. 2014 Sep 15;39(18):5451-4. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.005451. Opt Lett. 2014. PMID: 26466295
-
A Review of Security Evaluation of Practical Quantum Key Distribution System.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Feb 10;24(2):260. doi: 10.3390/e24020260. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantum communication with coherent states of light.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017 Aug 6;375(2099):20160235. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2016.0235. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017. PMID: 28652491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantum key distribution over 120 km using ultrahigh purity single-photon source and superconducting single-photon detectors.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 25;5:14383. doi: 10.1038/srep14383. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26404010 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum man-in-the-middle attack on the calibration process of quantum key distribution.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 9;8(1):4283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22700-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29523828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett C. H. & Brassard G. Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Paper presented at International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India. New York: IEEE. p.175–179 (1984).
-
- Shor P. W. & Preskill J. Simple Proof of Security of the BB84 Quantum Key Distribution Protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441–444 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Gottesman D., Lo H. K., Lütkenhaus N. & Preskill J. Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quantum Inf. Comput. 4, 325 (2004).
-
- Wang S. et al. 2 GHz clock quantum key distribution over 260 km of standard telecom fiber. Opt. Lett. 37, 1008–1010 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Namekata N., Adachi S. & Inoue S. 1.5 GHz single-photon detection at telecommunication wavelengths using sinusoidaly gated InGaAs/InP avalanche photodiode. Opt. Express 17, 6275–6282 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

