Emergent global patterns of ecosystem structure and function from a mechanistic general ecosystem model
- PMID: 24756001
- PMCID: PMC3995663
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001841
Emergent global patterns of ecosystem structure and function from a mechanistic general ecosystem model
Abstract
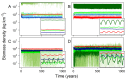
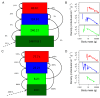
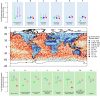
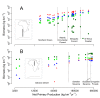
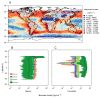
Anthropogenic activities are causing widespread degradation of ecosystems worldwide, threatening the ecosystem services upon which all human life depends. Improved understanding of this degradation is urgently needed to improve avoidance and mitigation measures. One tool to assist these efforts is predictive models of ecosystem structure and function that are mechanistic: based on fundamental ecological principles. Here we present the first mechanistic General Ecosystem Model (GEM) of ecosystem structure and function that is both global and applies in all terrestrial and marine environments. Functional forms and parameter values were derived from the theoretical and empirical literature where possible. Simulations of the fate of all organisms with body masses between 10 µg and 150,000 kg (a range of 14 orders of magnitude) across the globe led to emergent properties at individual (e.g., growth rate), community (e.g., biomass turnover rates), ecosystem (e.g., trophic pyramids), and macroecological scales (e.g., global patterns of trophic structure) that are in general agreement with current data and theory. These properties emerged from our encoding of the biology of, and interactions among, individual organisms without any direct constraints on the properties themselves. Our results indicate that ecologists have gathered sufficient information to begin to build realistic, global, and mechanistic models of ecosystems, capable of predicting a diverse range of ecosystem properties and their response to human pressures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: biodiversity synthesis. Washington, DC: World Resources Institute.
-
- Rodríguez JP, Brotons L, Bustamante J, Seoane J (2007) The application of predictive modelling of species distribution to biodiversity conservation. Divers Distrib 13: 243–251 doi:10.1111/j.1472-4642.2007.00356.x - DOI
-
- Thomas CD, Cameron A, Green RE, Bakkenes M, Beaumont LJ, et al. (2004) Extinction risk from climate change. Nature 427: 145–148 doi:10.1038/nature02121 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alkemade R, Oorschot M, Miles L, Nellemann C, Bakkenes M, et al. (2009) GLOBIO3: a framework to investigate options for reducing global terrestrial biodiversity loss. Ecosystems 12: 374–390 doi:10.1007/s10021-009-9229-5 - DOI
-
- Mace GM (2013) Ecology must evolve. Nature 503: 191–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

