Comparison of Parkinson risk in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with Gaucher disease and GBA heterozygotes
- PMID: 24756352
- PMCID: PMC4082726
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.313
Comparison of Parkinson risk in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with Gaucher disease and GBA heterozygotes
Abstract
Importance: Information on age-specific risk for Parkinson disease (PD) in patients with Gaucher disease (GD) and glucocerebrosidase (GBA) heterozygotes is important for understanding the pathophysiology of the genetic association and for counseling these populations.
Objective: To estimate the age-specific risk for PD in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with type 1 GD and in GBA heterozygotes.
Design, setting, and participants: The study included patients with GD from 2 tertiary centers, Shaare Zedek Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel (n = 332) and Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, New York (n = 95). GBA noncarrier non-PD spouse control participants were recruited at the Center for Parkinson's Disease at Columbia University, New York (n = 77). All participants were Ashekanzi Jewish and most patients (98.1%) with GD carried at least 1 N370S mutation.
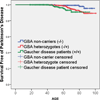
Main outcomes and measures: The main outcome measure was a diagnosis of PD. Diagnosis was established in patients with GD on examination. We used a validated family history interview that identifies PD with a sensitivity of 95.5% and specificity of 96.2% to identify PD in family members. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to estimate age-specific PD risk among patients with GD (n = 427), among their parents who are obligate GBA mutation carriers (heterozygotes, n = 694), and among noncarriers (parents of non-PD, non-GD control participants, n = 154). The age-specific risk was compared among groups using the log-rank test.
Results: Among those who developed PD, patients with GD had a younger age at onset than GBA heterozygotes (mean, 54.2 vs 65.2 years, respectively; P = .003). Estimated age-specific risk for PD at 60 and 80 years of age was 4.7% and 9.1% among patients with GD, 1.5% and 7.7% among heterozygotes, and 0.7% and 2.1% among noncarriers, respectively. The risk for PD was higher in patients with GD than noncarriers (P = .008, log-rank test) and in heterozygotes than noncarriers (P = .03, log-rank test), but it did not reach statistical significance between patients with GD and GBA heterozygotes (P = .07, log-rank test).
Conclusions and relevance: Patients with GD and GBA heterozygotes have an increased age-specific risk for PD compared with control individuals, with a similar magnitude of PD risk by 80 years of age; however, the number of mutant alleles may play an important role in age at PD onset.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mitsui J, Mizuta I, Toyoda A, et al. Mutations for Gaucher disease confer high susceptibility to Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2009 May;66(5):571–576. - PubMed
-
- Neudorfer O, Giladi N, Elstein D, et al. Occurrence of Parkinson's syndrome in type I Gaucher disease. QJM. 1996 Sep;89(9):691–694. - PubMed
-
- Lwin A, Orvisky E, Goker-Alpan O, LaMarca ME, Sidransky E. Glucocerebrosidase mutations in subjects with parkinsonism. Mol Genet Metab. 2004 Jan;81(1):70–73. - PubMed
-
- Aharon-Peretz J, Rosenbaum H, Gershoni-Baruch R. Mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene and Parkinson's disease in Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med. 2004 Nov 4;351(19):1972–1977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K02 NS080915/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02NS080915/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HL105333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R24HL105333-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029887/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR 029887/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS070608/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK095946/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK095946/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08-NS070608/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL102107-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical