Exercise for osteoarthritis of the hip
- PMID: 24756895
- PMCID: PMC10898220
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007912.pub2
Exercise for osteoarthritis of the hip
Abstract
Background: Current international treatment guidelines recommending therapeutic exercise for people with symptomatic hip osteoarthritis (OA) report are based on limited evidence.
Objectives: To determine whether land-based therapeutic exercise is beneficial for people with hip OA in terms of reduced joint pain and improved physical function and quality of life.
Search methods: We searched five databases from inception up to February 2013.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) recruiting people with hip OA and comparing some form of land-based therapeutic exercise (as opposed to exercises conducted in water) with a non-exercise group.
Data collection and analysis: Four review authors independently selected studies for inclusion. We resolved disagreements through consensus. Two review authors independently extracted data, assessed risk of bias and the quality of the body of evidence for each outcome using the GRADE approach. We conducted analyses on continuous outcomes (pain, physical function and quality of life) and dichotomous outcomes (proportion of study withdrawals).
Main results: We considered that seven of the 10 included RCTs had a low risk of bias. However, the results may be vulnerable to performance and detection bias as none of the RCTs were able to blind participants to treatment allocation and, while most RCTs reported blinded outcome assessment, pain, physical function and quality of life were participant self reported. One of the 10 RCTs was only reported as a conference abstract and did not provide sufficient data for the evaluation of bias risk.High-quality evidence from nine trials (549 participants) indicated that exercise reduced pain (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.38, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.55 to -0.20) and improved physical function (SMD -0.38, 95% CI -0.54 to -0.05) immediately after treatment. Pain and physical function were estimated to be 29 points on a 0- to 100-point scale (0 was no pain or loss of physical function) in the control group; exercise reduced pain by an equivalent of 8 points (95% CI 4 to 11 points; number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 6) and improved physical function by an equivalent of 7 points (95% CI 1 to 12 points; NNTB 6). Only three small studies (183 participants) evaluated quality of life, with overall low quality evidence, with no benefit of exercise demonstrated (SMD -0.07, 95% CI -0.23 to 0.36). Quality of life was estimated to be 50 points on a norm-based mean (standard deviation (SD)) score of 50 (10) in the general population in the control group; exercise improved quality of life by 0 points. Moderate-quality evidence from seven trials (715 participants) indicated an increased likelihood of withdrawal from the exercise allocation (event rate 6%) compared with the control group (event rate 3%), but this difference was not significant (risk difference 1%; 95% CI -1% to 4%). Of the five studies reporting adverse events, each study reported only one or two events and all were related to increased pain attributed to the exercise programme.The reduction in pain was sustained at least three to six months after ceasing monitored treatment (five RCTs, 391 participants): pain (SMD -0.38, 95% CI -0.58 to -0.18). Pain was estimated to be 29 points on a 0- to 100-point scale (0 was no pain) in the control group, the improvement in pain translated to a sustained reduction in pain intensity of 8 points (95% CI 4 to 12 points) compared with the control group (0 to 100 scale). The improvement in physical function was also sustained (five RCTs, 367 participants): physical function (SMD -0.37, 95% CI -0.57 to -0.16). Physical function was estimated to be 24 points on a 0- to 100-point scale (0 was no loss of physical function) in the control group, the improvement translated to a mean of 7 points (95% CI 4 to 13) compared with the control group.Only five of the 10 RCTs exclusively recruited people with symptomatic hip OA (419 participants). There was no significant difference in pain or physical function outcomes compared with five studies recruiting participants with hip or knee OA (130 participants).
Authors' conclusions: Pooling the results of these 10 RCTs demonstrated that land-based therapeutic exercise programmes can reduce pain and improve physical function among people with symptomatic hip OA.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
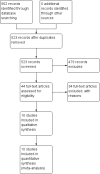













Update of
-
Exercise for osteoarthritis of the hip.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jul 8;(3):CD007912. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007912. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 22;(4):CD007912. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007912.pub2. PMID: 19588445 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abbott 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Abbott JH, Robertson MC, Chapple C, Pinto D, Wright AA, Leon de la Barra S, et al. Manual therapy, exercise therapy, or both, in addition to usual care, for osteoarthritis of the hip or knee: a randomized controlled trial. A: clinical effectiveness. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2013;21:525‐34. - PubMed
Carlson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Carlson NL, Christopherson Z, Arnall E, Mohn S, Holton K, Marshall L, et al. A pilot study of the effects of strength and aerobic conditioning in patients with hip osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2011;19:S212.
Fernandes 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fernandes L, Storheim K, Sandvik L, Nordsletter L, Risberg MA. Efficacy of patient education and supervised exercise vs patient education alone in patients with hip osteoarthritis: a single blind randomized clinical trial. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2010;18:1237‐43. - PubMed
Foley 2003 {published data only}
Fransen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fransen M, Nairn L, Winstanley J, Lam P, Edmonds J. The Physical Activity for Osteoarthritis Management (PAFORM) study. A randomised controlled clinical trial evaluating hydrotherapy and Tai Chi classes. Arthritis Care and Research 2007;57:407‐14. - PubMed
French 2013 {published data only}
-
- French HP, Cusak T, Brennan A, Caffrey A, Conroy R, Cuddy V, et al. Exercise and manual physiotherapy arthritis research trial (EMPART) for osteoarthritis of the hip: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2013;94:302‐14. - PubMed
Hopman‐Rock 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hopman‐Rock M, Westhoff M. The effects of a health educational and exercise program for older adults with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Journal of Rheumatology 2000;27:1947‐54. - PubMed
Juhakoski 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Juhakoski R, Tenhonen S, Malmivaara A, Kiviniemi V, Anttonen T, Arokoski J. A pragmatic randomized controlled study of the effectiveness and cost consequences of exercise therapy in hip osteoarthritis. Clinical Rehabilitation 2011;25:370‐83. - PubMed
Tak 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tak E, Staats P, Hespen A, Hopman‐Rock A. The effects of an exercise program for older adults with osteoarthritis of the hip. Journal of Rheumatology 2005;6:1106‐13. - PubMed
van Baar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Baar ME, Dekker J, Oostendorp RAB, Bijl D, Voorn TB, Lemmens JAM, et al. The effectiveness of exercise therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Rheumatology 1998;25:2432‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbott 2012 {published data only}
-
- Abbott JH, Pinto D, Robertson MC. Exercise therapy, manual therapy, or both, for management of osteoarthritis of the hip or knee: economic evaluation alongside a randomized clinical trial. Value in Health 2012;15:A447.
Angst 2001 {published data only}
Boeer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Boeer J, Mueller O, Krauss I, Haupt G, Axmann D, Horstmann T. Effects of a sensory‐motor exercise program for older adults with osteoarthritis or prosthesis of the hip using measurements made by the posturomed oscillatory platform. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy 2010;33:10‐5. - PubMed
Brantingham 2012 {published data only}
-
- Brantingham JW, Parkin‐Smith G, Cassa TK, Globe GA, Globe D, Pollard H, et al. Full kinetic chain manual and manipulative therapy plus exercise compared with targeted manual and manipulative therapy plus exercise for symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hip: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2012;93:259‐67. - PubMed
Cochrane 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cochrane T, Davey RC, Matthes Edwards SM. Randomised controlled trial of the cost‐effectiveness of water‐based therapy for lower limb osteoarthritis. Health Technology Assessment 2005;9:1‐114. - PubMed
Coupe 2007 {published data only}
de Jong 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jong ORW, Hopman‐Rock M, Tak E, Klazinga N. An implementation study of two evidence‐based exercise and health education programmes for older adults with osteoarthritis of the knee and hip. Health Education Research 2004;19:316. - PubMed
Eitzen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Eitzen I, Fernandes L, Rydevik K, Nordsletten L, Risberg M. Gait characteristics and potential effect of supervised exercise therapy in hip osteoarthritis patients with mild to moderate pain. A randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2011;19:S17‐8.
Green 1993 {published data only}
-
- Green J, McKenna F, Redfern EJ, Chamberlain MA. Home exercises are as effective as outpatient hydrotherapy for osteoarthritis of the hip. British Journal of Rheumatology 1993;32:812‐5. - PubMed
Halbert 2001 {published data only}
-
- Halbert J, Crotty M, Weller D, Ahern M, Silagy C. Primary care‐based physical activity programs: effectiveness in sedentary older patients with osteoarthritis symptoms. Arthritis Care and Research 2001;45:228‐34. - PubMed
Haslam 2001 {published data only}
-
- Haslam R. A comparison of acupuncture with advice and exercises on the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip ‐ a randomised controlled trial. Acupuncture Medicine 2001;19:19‐26. - PubMed
Heuts 2005 {published data only}
-
- Heuts PH, Bie R, Drietelaar M, Aretz K, Hopman‐Rock M, Bastiaenen CH, et al. Self‐management in osteoarthritis of hip or knee: a randomized clinical trial in a primary healthcare setting. Journal of Rheumatology 2005;32:543‐9. - PubMed
Hinman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hinman RS, Heywood SE, Day AR. Aquatic physical therapy for hip and knee osteoarthritis: results of a single‐blind randomized controlled trial. Physical Therapy 2007;87:32‐43. - PubMed
Hoeksma 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hoeksma HL, Dekker J, Ronday HK, Heering A, Lubbe N, Vel C, et al. Comparison of manual therapy and exercise therapy in osteoarthritis of the hip: a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Rheumatism 2004;51:722‐9. - PubMed
Hoeksma 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hoeksma HL, Dekker J, Ronday HK, Breedveld RC, Ende CH. Manual therapy in osteoarthritis of the hip: outcome in subgroups of patients. Rheumatology 2005;44:461‐4. - PubMed
Hoeksma 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hoeksma HL, Ende CH, Breedveld FC, Ronday HK, Dekker J. A comparison of the OARSI response criteria with patient's global assessment in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip treated with a non‐pharmacological intervention. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2006;14:77‐81. - PubMed
Klasbo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Klasbo M, Larsson G, Harmas‐Ringdahl K. Promising outcome of a hip school for patients with hip dysfunction. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2003;49:321‐7. - PubMed
Koybashi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Koybasi M, Borman P, Kocaoglu S, Ceceli E. The effect of additional therapeutic ultrasound in patients with primary hip osteoarthritis: a randomized placebo‐controlled study. Clinical Rheumatology 2010;29:1387‐94. - PubMed
Lin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lin SY, Davey RC, Cochrane T. Community rehabilitation for older adults with osteoarthritis of the lower limb: a controlled clinical trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;18:92‐101. - PubMed
Pisters 2010a {published data only}
-
- Pisters MF, Veenhof C, Bakker DH, Schellevis FG, Dekker J. Behavioural graded activity results in better exercise adherence and more physical activity than usual care in people with osteoarthritis: a cluster‐randomised trial. Journal of Physiotherapy 2010;56:41‐7. - PubMed
Pisters 2010b {published data only}
-
- Pisters MF, Veenhof C, Schellevis FG, Bakker DH, Dekker J. Long‐term effectiveness of exercise therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee: a randomized controlled trial comparing two different physical therapy interventions. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2010;18:1019‐26. - PubMed
Ravaud 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ravaud P, Giraudeau B, Logeart I, Larguier JS, Rolland D, Treves R, et al. Management of osteoarthritis with an unsupervised home based exercise programme and/or patient administered assessment tools. A cluster randomised controlled trial with a 2x2 factorial design. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2004;63:703‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Rooks 2006 {published data only}
-
- Rooks DS, Huang J, Bierbaum BE, Bolus SA, Rubano J, Connolly CE, et al. Effect of preoperative exercise on measures of functional status in men and women undergoing total hip and knee arthroplasty. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;55:700‐8. - PubMed
Song 2010 {published data only}
Steenstrup 2012 {published data only}
-
- Steenstrup B, Roudesli M, Beaufils J. Evaluation of a specific protocol of ambulatory physiotherapy for hip osteoarthritis [Evaluation d'un protocole specifique de kinesitherapie ambulatoire de la coxarthrose]. Kinesitherapie 2012;12:67‐77.
Steinhilber 2012 {published data only}
-
- Steinhilber B, Haupt G, Miller R, Boeer J, Grau S, Janssen P, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of an 8‐week progressive home‐based strengthening exercise program in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and/or total hip joint replacement: a preliminary trial. Clinical Rheumatology 2012;31:511‐9. - PubMed
Stener‐Victoria 2004 {published data only}
-
- Stener‐Victoria E, Kruse C, Jung K. Comparison between electro‐acupuncture and hydrotherapy, both in combination with patient education and patient education alone, on the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clinical Journal of Pain 2004;20:179‐85. - PubMed
Svege 2010 {published data only}
-
- Svege IC, Fernandes L, Nordsletten L, Risberg M. Long term effect of a supervised exercise program and patient education for patients with hip osteoarthritis. A randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2010;18:S142. - PubMed
Svege 2011 {published data only}
-
- Svege IC, Fernandes L, Nordsletten L, Risberg M. Time to total hip replacement surgery after supervised exercise and patient education in patients with hip osteoarthritis. A randomized intervention study with between 3.5 and 6 years follow up. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2011;19:S44‐5.
Sylvester 1989 {published data only}
-
- Sylvester KL. Investigation of the effect of hydrotherapy in the treatment of osteoarthritic hips. Clinical Rehabilitation 1989;4:223‐8.
Uesugi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Uesugi Y, Koyanagi J, Nishii T, Hayashi S, Fujishiro T, Takagi K, et al. Clinical trial of step‐up exercise therapy using DVD for patients with hip osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2012;20:S265.
van Baar 2001 {published data only}
Veenhof 2006 {published data only}
-
- Veenhof C, Koke AJ, Dekker J, Oostendorp RA, Bijlsma JW, Tulder MW, et al. Effectiveness of behavioural graded activity in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and/or knee: a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Care and Research 2006;55:925‐34. - PubMed
Wang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wang T‐J, Belza B, Thompson FE, Whitney JD, Bennett K. Effects of aquatic exercise on flexibility, strength and aerobic fitness in adults with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2007;57:141‐52. - PubMed
Additional references
Arden 2006
-
- Arden N, Nevitt MC. Osteoarthritis: epidemiology. Best Practice and Research Clinical Rheumatology 2006;20:3‐25. - PubMed
Arokoski 2002
-
- Arokoski MH, Arokoski JP, Haara M, Kankaanpaa M, Vesterinen M, Niemitukia LH, et al. Hip muscle strength and muscle cross sectional area in men with and without hip osteoarthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29:2185‐95. - PubMed
Bellamy 1997
-
- Bellamy N, Kirwan J, Boers M, Brooks P, Strand V, Tugwell P, et al. Recommendations for a core set of outcome measures for future phase III clinical trials in knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis. Consensus development at OMERACT III. Journal of Rheumatology 1997;24:799‐802. - PubMed
Busija 2010
-
- Busija L, Bridgett L, Williams S, Osborne R, Buchbinder R, March L, et al. Burden of musculoskeletal conditions: osteoarthritis. Best Practice and Research in Clinical Rheumatology 2010;24:757‐69. - PubMed
Cohen 1977
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences. New York: Academic, 1977.
Croft 2002
-
- Croft P, Lewis M, Wynn Jones C, Coggon D, Cooper C. Health status in patients awaiting hip replacement for osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2002;41:1001‐7. - PubMed
Dawson 2004
-
- Dawson J, Linsell L, Zondervan K, Rose R, Randall T, Carr A. Epidemiology of hip and knee pain and its impact on overall health status in older adults. Rheumatology 2004;43:497‐504. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins J, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Fransen 2011
-
- Fransen M, Agaliotis M, Bridgett L, Mackey M. Hip and knee pain. Occupational risk factors. Best Practice and Research in Clinical Rheumatology 2011;25:81‐101. - PubMed
Hernandez‐Molina 2008
Juni 2006
-
- Juni P, Reichenbach S, Dieppe P. Osteoarthritis: Rational approach to treating the individual. Best Practice & Research in Clinical Rheumatology 2006;20:721‐40. - PubMed
Lane 2007
-
- Lane NE. Osteoarthritis of the hip. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357:1413‐21. - PubMed
Lawrence 1998
-
- Lawrence RC, Helmick CG, Arnett FC. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disorders in the United States. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1998;41:778‐99. - PubMed
Moskowitz 2007
-
- Moskowitz RW, Altman RD, Hochberg MC, Buckwalter JA, Goldberg VM. Osteoarthritis. Diagnosis and medical/surgical management. Fourth. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007.
Odding 1998
Reichenbach 2007
-
- Reichenbach S, Sterchi R, Scherer M, Trelle S, Burgi E, Burgi U, et al. Meta‐analysis: chondroitin for osteoarthritis of the knee hip. Annals of Internal Medicine 2007;146:580‐90. - PubMed
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Suetta 2007
-
- Suetta C, Aagaard P, Magnusson SP, Andersen LL, Sipila S, Rosted A, et al. Muscle size, neuromuscular activation, and rapid force characteristics in elderly men and women: effects of unilateral long‐term disuse due to hip osteoarthritis. Journal of Applied Physiology 2007;102:942‐8. - PubMed
Zhang 2008
-
- Zhang W, Moskowitz R, Nuki G, Abramson S, Altman R, Arden N, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence‐based, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2008;16:137‐62. - PubMed
Zhang 2010
-
- Zhang W, Nuki G, Moskowitz RW, Abramson S, Altman RD, Arden NK, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: Part III: changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2010;18:476‐99. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Fransen 2001
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

