Amyloid and the macrophage: it's all about local production of IL-1β
- PMID: 24757195
- PMCID: PMC3994949
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-0003
Amyloid and the macrophage: it's all about local production of IL-1β
Figures
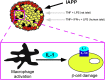
Comment on
-
Resident macrophages mediate islet amyloid polypeptide-induced islet IL-1β production and β-cell dysfunction.Diabetes. 2014 May;63(5):1698-711. doi: 10.2337/db13-0863. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24222351
References
-
- Bendtzen K, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Nerup J, Nielsen JH, Dinarello CA, Svenson M. Cytotoxicity of human pI 7 interleukin-1 for pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Science 1986;232:1545–1547 - PubMed
-
- Mandrup-Poulsen T, Bendtzen K, Nerup J, Egeberg J, Nielsen JH. Mechanisms of pancreatic islet cell destruction. Dose-dependent cytotoxic effect of soluble blood mononuclear cell mediators on isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy 1986;41:250–259 - PubMed
-
- Corbett JA, Wang JL, Sweetland MA, Lancaster JR, Jr, McDaniel ML. Interleukin 1 beta induces the formation of nitric oxide by beta-cells purified from rodent islets of Langerhans. Evidence for the beta-cell as a source and site of action of nitric oxide. J Clin Invest 1992;90:2384–2391 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Southern C, Schulster D, Green IC. Inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha via an L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide generating mechanism. FEBS Lett 1990;276:42–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

