The Comparisons of Surgical Outcomes and Clinical Characteristics between the Far Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniations and the Paramedian Lumbar Disc Herniations
- PMID: 24757478
- PMCID: PMC3941755
- DOI: 10.14245/kjs.2013.10.3.155
The Comparisons of Surgical Outcomes and Clinical Characteristics between the Far Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniations and the Paramedian Lumbar Disc Herniations
Abstract
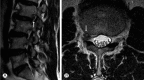
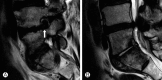
Objective: The purpose of this study is to analyze clinical characteristics and surgical outcomes of the far lateral and the paramedian disc herniations.
Methods: The 88 patients who underwent an operation for lumbar disc herniations were reviewed. Visual analogue scale of leg and back pain, occurrence of sensory dysesthesia and motor deficit before and after operations were used to compare the far lateral with the paramedian disc herniations.
Results: Statistically, the far lateral herniations had more severe radicular leg pain and showed more frequent occurrence of sensory dysesthesia than paramedian herniations before operation (p<0.05). In the far lateral herniation group, preoperatively, 15 patients (75%) had sensory dysesthesia and among them, 4 patients (27%) showed improvement. In the paramedian herniation group, preoperatively, 25 patients (37%) had sensory dysesthesia and among them, 21 patients (84%) showed improvement. The degree of improvement in sensory dysesthesia was statistically higher in paramedian herniation group (p<0.05). In the far lateral herniation group, preoperatively, 11 patients (55%) had motor deficit and among them, 10 patients (91%) showed improvement. In the paramedian herniations, preoperatively, 29 patients (43%) had motor deficit and among them, 25 patients (86%) showed improvement. The degree of improvement in motor deficit was not statistically significant between groups (p>0.05).
Conclusion: Preoperatively, the far lateral herniations had more severe radicular leg pain and frequent occurrence of sensory dysesthesia. Postoperatively, the sensory dysesthesia was less improved and back pain was more severe in the far lateral herniations.
Keywords: Clinical characteristics; Far lateral disc herniation; Paramedian disc herniation; Surgical outcomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-term follow-up results of surgically treated patients with foraminal and far lateral disc herniations.Br J Neurosurg. 2023 Feb;37(1):49-52. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2021.1874293. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Br J Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 33502266
-
Evaluation of the effectiveness of transforaminal epidural steroid injection in far lateral lumbar disc herniations.Ideggyogy Sz. 2021 Jan 30;74(1-2):27-32. doi: 10.18071/isz.74.0027. Ideggyogy Sz. 2021. PMID: 33497058 English.
-
Efficacy of epidural steroid injections and evaluation of surgical and anesthetic approaches in far-lateral disc herniations.Pain Manag. 2023 Feb;13(2):95-104. doi: 10.2217/pmt-2022-0035. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Pain Manag. 2023. PMID: 36718770
-
Far lateral lumbar disc herniation part 1: Imaging, neurophysiology and clinical features.World J Orthop. 2021 Dec 18;12(12):961-969. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i12.961. eCollection 2021 Dec 18. World J Orthop. 2021. PMID: 35036338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nursing review section of Surgical Neurology International: Part 1 lumbar disc disease.Surg Neurol Int. 2017 Dec 11;8:301. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_151_17. eCollection 2017. Surg Neurol Int. 2017. PMID: 29296287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Five-year outcomes and predictive factors of transforaminal full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(48):e13454. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013454. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30508966 Free PMC article.
-
A Modified Approach of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (PELD) for Far Lateral Disc Herniation at L5-S1 with Foot Drop.Korean J Pain. 2016 Jan;29(1):57-61. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.57. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 26839673 Free PMC article.
-
Transforaminal Epidural Injection for Far Lateral Lumbar Disc Herniations: An Alternative to Surgery or Just a Delay?Cureus. 2024 Jan 18;16(1):e52530. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52530. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38371082 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Lumbosacral Lateral Disc Herniation in Comparison With Those of Medial Disc Herniation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Feb;95(7):e2733. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002733. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26886615 Free PMC article.
-
Comparable effectiveness of transforaminal endoscopic spine system technique combined with selective nerve root block between far lateral lumbar disc herniation and central or paracentral herniation.Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022;33(3):513-520. doi: 10.52312/jdrs.2022.761. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022. PMID: 36345178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdullah A, Ditto EW, III, Byrd EB, Williams R. Extreme-lateral lumbar disc herniations: clinical syndrome and special problems of diagnosis. J Neurosurg. 1974;41:229–234. - PubMed
-
- Chang SB, Lee SH, Ahn Y, Kim JM. Risk factor for unsatisfactory outcome after lumbar foraminal and far lateral microdecompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:1163–1167. - PubMed
-
- Choi JW, Jang TW, Shin IY, Moon SM, Hwang HS, Jeong JH. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Low Back Pain. Korean J Spine. 2011;8:141–147.
-
- Epstein NE. Evaluation of varied surgical approaches used in the management of 170 far-lateral lumbar disc herniations: indications and results. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:648–656. - PubMed
-
- Epstein NE. Foraminal and far lateral lumbar disc herniations: surgical alternatives and outcome measures. Spinal Cord. 2002;40:491–500. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

