Omega-3 fatty acids and depression: scientific evidence and biological mechanisms
- PMID: 24757497
- PMCID: PMC3976923
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/313570
Omega-3 fatty acids and depression: scientific evidence and biological mechanisms
Abstract
The changing of omega-6/omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in the food supply of Western societies occurred over the last 150 years is thought to promote the pathogenesis of many inflammatory-related diseases, including depressive disorders. Several epidemiological studies reported a significant inverse correlation between intake of oily fish and depression or bipolar disorders. Studies conducted specifically on the association between omega-3 intake and depression reported contrasting results, suggesting that the preventive role of omega-3 PUFA may depend also on other factors, such as overall diet quality and the social environment. Accordingly, tertiary prevention with omega-3 PUFA supplement in depressed patients has reached greater effectiveness during the last recent years, although definitive statements on their use in depression therapy cannot be yet freely asserted. Among the biological properties of omega-3 PUFA, their anti-inflammatory effects and their important role on the structural changing of the brain should be taken into account to better understand the possible pathway through which they can be effective both in preventing or treating depression. However, the problem of how to correct the inadequate supply of omega-3 PUFA in the Westernized countries' diet is a priority in order to set food and health policies and also dietary recommendations for individuals and population groups.
Figures
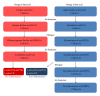
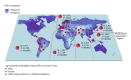
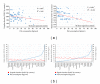
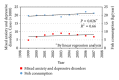
References
-
- Simopoulos AP. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy. 2002;56(8):365–379. - PubMed
-
- Simopoulos AP. Executive summary of the international conference on genetic variation and nutrition. World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics. 1990;63:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Simopoulos AP, Ordovas J. Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics. Vol. 93. Washington, DC, USA: Karger; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

