Projections of total hip replacement in Sweden from 2013 to 2030
- PMID: 24758323
- PMCID: PMC4062789
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2014.913224
Projections of total hip replacement in Sweden from 2013 to 2030
Abstract
Background and purpose: The continuously increasing demand for joint replacement surgery in the past decades imposes higher constraints on the budgets of hospitals and healthcare providers. We undertook an analysis of historical trends in total hip replacement performed in Sweden between 1968 and 2012 in order to provide projections of future demand.
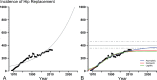
Data and methods: We obtained data on total hip replacements registered every year and on the evolution of the Swedish population between 1968 and 2012. We assumed the existence of a maximum incidence. So we adopted a regression framework that assumes the existence of an upper limit of total hip replacement incidence.
Results: We found that the incidence of total hip replacement will continue to increase until a projected upper incidence level of about 400 total hip replacements per 10(5) Swedish residents aged 40 years and older will be reached around the year 2107. In 2020, the estimated incidence of total hip replacement will be 341 (95% prediction interval (PI): 302-375) and in 2030 it will be 358 (PI: 317-396). Using official forecasted population growth data, about 18,000 operations would be expected to be performed in 2020 and 20,000 would be expected to be performed in 2030.
Interpretation: Growing incidence, population growth, and increasing life expectancy will probably result in increased demand for hip replacement surgery. Our findings could serve as a basis for decision making.
Figures

References
-
- Berger A, Bozic K, Stacey B, Edelsberg J, Sadosky A, Oster G. Patterns of pharmacotherapy and health care utilization and costs prior ... . Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(8):2268–75. - PubMed
-
- Bini SA, Sidney S, Sorel M. Slowing demand for total joint arthroplasty in a population of 3.2 million . J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(6):124–8. - PubMed
-
- Bozdogan H. Model selection and Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)-The general-theory and its analytical extensions. Psychometrika. 1987;3:345–70.
-
- Davies C, Briggs A, Lorgelly P, Garellick G, Malchau H. The “hazards” of extrapolating survival curves . Med Decis Making. 2013;33(3):369–80. - PubMed
-
- Elzhov TV, Mullen KM, Spiess AN, Bolker B. minpack.lm: R interface to the Levenberg-Marquardt nonlinear least-squares algorithm found in MINPACK, plus support for bounds. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=minpack.lm R package version. 2013:11–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
