A novel pathogenic peptide of thyroglobulin (2208-2227) induces autoreactive T-cell and B-cell responses in both high and low responder mouse strains
- PMID: 24758369
- PMCID: PMC4008237
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12254
A novel pathogenic peptide of thyroglobulin (2208-2227) induces autoreactive T-cell and B-cell responses in both high and low responder mouse strains
Abstract
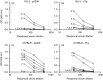
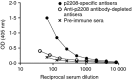
Experimental autoimmune thyroiditis (EAT) is commonly induced by thyroglobulin (Tg) or Tg peptides in mice genetically susceptible to thyroiditis. In the present study, we investigated the immunogenic and pathogenic potential of a novel 20mer human Tg peptide, p2208 (amino acids 2208-2227), in mouse strains classified as low (LR) or high (HR) responders in EAT. The peptide was selected for its content in overlapping binding motifs for MHC class II products, associated with either resistance (A(b)), or susceptibility (A(s), E(k)) to EAT. We therefore immunized LR BALB/c (H-2(d)) and C57BL/6 (H-2(b)) strains, as well as HR CBA/J (H-2(k)) and SJL/J (H-2(s)) mice with 100 nmol of p2208 in adjuvant and collected their sera, lymph nodes and thyroid glands for further analysis. The p2208 peptide was found to contain B-cell and cryptic T-cell epitope(s) in two of the four strains examined, one LR and one HR. Specifically, it elicited direct EAT in C57BL/6 mice (two of seven mice, infiltration index 1-3), as well as in SJL/J mice (two of six mice, infiltration index 1-2). Such an EAT model could provide insights into the immunoregulatory cascades taking place in resistant hosts.
Keywords: T-cell epitopes; experimental autoimmune thyroiditis; high/low responders; pathogenic thyroglobulin peptides; resistant/susceptible strains.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fine epitope mapping within the pathogenic thyroglobulin peptide 2340-2359: minimal epitopes retaining antigenicity across various MHC haplotypes are not necessarily immunogenic.Immunology. 2012 Mar;135(3):245-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03538.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22098450 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct genetic pattern of mouse susceptibility to thyroiditis induced by a novel thyroglobulin peptide.Immunogenetics. 1994;39(1):21-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00171793. Immunogenetics. 1994. PMID: 8225435
-
Identification of a thyroiditogenic sequence within the thyroglobulin molecule.J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):1039-44. J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1378862
-
T cell mapping of one epitope from thyroglobulin inducing experimental autoimmune thyroiditis (EAT).Int Rev Immunol. 1992;9(2):125-33. doi: 10.3109/08830189209061787. Int Rev Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1283174 Review.
-
[Identification and immunopathogenicity of a common T cell epitope between human thyroglobulin and human thyroid peroxidase].Nihon Rinsho. 1994 Apr;52(4):1063-8. Nihon Rinsho. 1994. PMID: 7515121 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Is Graves' disease a primary immunodeficiency? New immunological perspectives on an endocrine disease.BMC Med. 2017 Sep 25;15(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0939-9. BMC Med. 2017. PMID: 28942732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charreire J. Immune mechanisms in autoimmune thyroiditis. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:263–334. - PubMed
-
- Rose NR, Twarog FJ, Crowle AJ. Murine thyroiditis: importance of adjuvant and mouse strain for the induction of thyroid lesions. J Immunol. 1971;106:698–704. - PubMed
-
- Vladutiu AO, Rose NR. Cellular basis of the genetic control of immune responsiveness to murine thyroglobulin in mice. Cell Immunol. 1975;17:106–13. - PubMed
-
- Vladutiu AO, Rose NR. Autoimmune murine thyroiditis relation to histocompatibility (H-2) type. Science. 1971;174:1137–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

