Clinical evaluation of cetuximab combined with an S-1 and oxaliplatin regimen for Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 24758484
- PMCID: PMC4020605
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-115
Clinical evaluation of cetuximab combined with an S-1 and oxaliplatin regimen for Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: The prognosis of patients with advanced gastric cancer is poor. The goal of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combination therapy of cetuximab and S-1 combined with oxaliplatin (SOX) in Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer.
Methods: For patients in the experimental group (cetuximab in combination with SOX (Ce-SOX), 30 patients), once-weekly cetuximab (400 mg/m2 at the first infusion then 250 mg/m2 every week) was administered. For patients in both the control (SOX alone, 26 patients) and experimental groups, oxaliplatin (100 mg/m2) was administered intravenously on day 1, while S-1 (80 mg/m2/day) was given orally twice daily for 14 days. The endpoints of this study included progression-free survival, response rate, and disease-control rate.
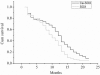
Results: There was no statistically significant difference in response rate between the Ce-SOX and SOX groups (54.8% versus 44%, P=0.225). The difference in disease-control rate was also statistically insignificant between the two groups (87.1% versus 76%, P=0.162). Median progression-free survival in the Ce-SOX group was significantly higher than that in the SOX group (12.8 versus 10.1 months, P=0.007). The median overall survival of the Ce-SOX group and SOX group was 14.0 and 12.2 months, respectively (P=0.043). The one-year survival rate for the Ce-SOX group was 57% compared to 40% in the SOX group. There was no statistical difference in the grade 3 or 4 adverse effects between the two groups.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the cetuximab combined with SOX regimen is feasible and shows promising efficacy with tolerable adverse effects in Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Wang X, Wang ML, Zhou LY, Lu XY, Yang JF, Yu HG. Randomized phase II study comparing paclitaxel with S-1 vs. S-1 as first-line treatment in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013;15:836–842. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous