Natural dibenzo-α-pyrones and their bioactivities
- PMID: 24759070
- PMCID: PMC6271090
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19045088
Natural dibenzo-α-pyrones and their bioactivities
Abstract
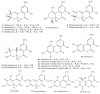
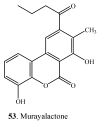
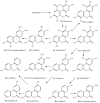
Natural dibenzo-α-pyrones are an important group of metabolites derived from fungi, mycobionts, plants and animal feces. They exhibit a variety of biological activities such as toxicity on human and animals, phytotoxicity as well as cytotoxic, antioxidant, antiallergic, antimicrobial, antinematodal, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties. Dibenzo-α-pyrones are biosynthesized via the polyketide pathway in microorganisms or metabolized from plant-derived ellagitannins and ellagic acid by intestinal bacteria. At least 53 dibenzo-α-pyrones have been reported in the past few decades. This mini-review aims to briefly summarize the occurrence, biosynthesis, biotransformation, as well as their biological activities and functions. Some considerations related to synthesis, production and applications of dibenzo-α-pyrones are also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Tanahashi T., Kuroishi M., Kuwahara A., Nagakura N., Hamada N. Four phenolics from the cultured lichen mycobiont of Graphis scripta var. pulverulenta. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997;45:1183–1185. doi: 10.1248/cpb.45.1183. - DOI
-
- Shirataki Y., Toda S. Antioxidative effects of dibenzo-α-pyrones in fruits of Trapa natans on lipid peroxidation. Nat. Med. 2001;55:247–250.
-
- Liang D., Luo H., Liu Y.-F., Hao Z.-Y., Wang Y., Zhang C.-L., Zhang Q.-J., Chen R.-Y., Yu D.-Q. Lysilactones A-C, three 6H-dibenzo[b,d]pyran-6-one glycosides from Lysimachia clethroides, total synthesis of lysilactone A. Tetrahedron. 2013;69:2093–2097. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2013.01.029. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

