Therapeutic targeting of BET bromodomain proteins in castration-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 24759320
- PMCID: PMC4075966
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13229
Therapeutic targeting of BET bromodomain proteins in castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
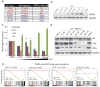
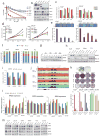
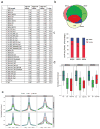
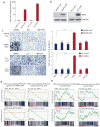
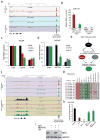
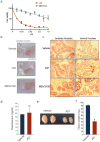
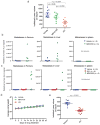
Men who develop metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) invariably succumb to the disease. Progression to CRPC after androgen ablation therapy is predominantly driven by deregulated androgen receptor (AR) signalling. Despite the success of recently approved therapies targeting AR signalling, such as abiraterone and second-generation anti-androgens including MDV3100 (also known as enzalutamide), durable responses are limited, presumably owing to acquired resistance. Recently, JQ1 and I-BET762 two selective small-molecule inhibitors that target the amino-terminal bromodomains of BRD4, have been shown to exhibit anti-proliferative effects in a range of malignancies. Here we show that AR-signalling-competent human CRPC cell lines are preferentially sensitive to bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) inhibition. BRD4 physically interacts with the N-terminal domain of AR and can be disrupted by JQ1 (refs 11, 13). Like the direct AR antagonist MDV3100, JQ1 disrupted AR recruitment to target gene loci. By contrast with MDV3100, JQ1 functions downstream of AR, and more potently abrogated BRD4 localization to AR target loci and AR-mediated gene transcription, including induction of the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion and its oncogenic activity. In vivo, BET bromodomain inhibition was more efficacious than direct AR antagonism in CRPC xenograft mouse models. Taken together, these studies provide a novel epigenetic approach for the concerted blockade of oncogenic drivers in advanced prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Comment in
-
Prostate cancer: novel targeting of androgen signalling in CRPC.Nat Rev Urol. 2014 Jun;11(6):303. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2014.107. Epub 2014 May 13. Nat Rev Urol. 2014. PMID: 24818852 No abstract available.
-
Prostate cancer: BETting on epigenetic therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Jun;14(6):384-5. doi: 10.1038/nrc3750. Epub 2014 May 15. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24827504 No abstract available.
-
BETting on a new prostate cancer treatment.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(13):2015-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.29459. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24905827 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
What is the next generation therapeutic strategy for castration-resistant prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2015 Mar-Apr;17(2):223-4. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.143311. Asian J Androl. 2015. PMID: 25432503 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

