Tunica albuginea allograft: a new model of LaPeyronie's disease with penile curvature and subtunical ossification
- PMID: 24759578
- PMCID: PMC4104088
- DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.125900
Tunica albuginea allograft: a new model of LaPeyronie's disease with penile curvature and subtunical ossification
Abstract
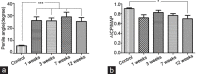
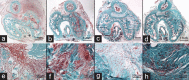
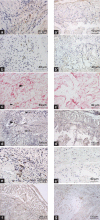
The pathophysiology of LaPeyronie's disease (PD) is considered to be multifactorial, involving genetic predisposition, trauma, inflammation and altered wound healing. However, these factors have not yet been validated using animal models. In this study, we have presented a new model obtained by tunica albuginea allograft. A total of 40, 16-week-old male rats were used. Of these, 8 rats served as controls and underwent a 10 × 2-mm-wide tunical excision with subsequent autografting, whereas the remaining 32 underwent the same excision with grafting of the defect with another rat's tunica. Morphological and functional testing was performed at 1, 3, 7 and 12 weeks after grafting. Intracavernous pressure, the degree of penile curvature and elastic fiber length were evaluated for comparison between the allograft and control groups. The tissues were obtained for histological examination. The penile curvature was significantly greater in the allografted rats as compared with the control rats. The erectile function was maintained in all rats, except in those assessed at 12 weeks. The elastin fiber length was decreased in the allografted tunica as compared to control. SMAD2 expression was detected in the inner part of the allograft, and both collagen-II- and osteocalcin-positive cells were also noted. Tunica albuginea (TA) allograft in rats is an excellent model of PD. The persistence of curvature beyond 12 weeks and the presence of ossification in the inner layer of the TA were similar to those observed in men with PD. Validation studies using this animal model would aid understanding of the PD pathophysiology for effective therapeutic interventions.
Figures


Comment in
-
Solving a bottleneck in animal models of Peyronie's disease.Asian J Androl. 2014 Jul-Aug;16(4):639. doi: 10.4103/1008-682x.126395. Asian J Androl. 2014. PMID: 24759583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Schwarzer U, Sommer F, Klotz T, Braun M, Reifenrath B, et al. The prevalence of Peyronie's disease: results of a large survey. BJU Int. 2001;88:727–30. - PubMed
-
- Mulhall JP, Creech SD, Boorjian SA, Ghaly S, Kim ED, et al. Subjective and objective analysis of the prevalence of Peyronie's disease in a population of men presenting for prostate cancer screening. J Urol. 2004;171:2350–3. - PubMed
-
- Rosen R, Catania J, Lue T, Althof S, Henne J, et al. Impact of Peyronie's disease on sexual and psychosocial functioning: qualitative findings in patients and controls. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1977–84. - PubMed
-
- Bella AJ, Perelman MA, Brant WO, Lue TF. Peyronie's disease (CME) J Sex Med. 2007;4:1527–38. - PubMed
-
- Shindel AW, Lue TF. Peyronie's disease: past, present, future? Curr Urol Rep. 2008;9:425–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

