Ezh2 regulates transcriptional and posttranslational expression of T-bet and promotes Th1 cell responses mediating aplastic anemia in mice
- PMID: 24760151
- PMCID: PMC4075972
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302943
Ezh2 regulates transcriptional and posttranslational expression of T-bet and promotes Th1 cell responses mediating aplastic anemia in mice
Abstract
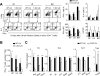
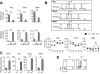
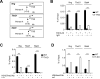
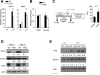
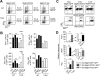
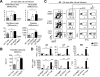
Acquired aplastic anemia (AA) is a potentially fatal bone marrow (BM) failure syndrome. IFN-γ-producing Th1 CD4(+) T cells mediate the immune destruction of hematopoietic cells, and they are central to the pathogenesis. However, the molecular events that control the development of BM-destructive Th1 cells remain largely unknown. Ezh2 is a chromatin-modifying enzyme that regulates multiple cellular processes primarily by silencing gene expression. We recently reported that Ezh2 is crucial for inflammatory T cell responses after allogeneic BM transplantation. To elucidate whether Ezh2 mediates pathogenic Th1 responses in AA and the mechanism of Ezh2 action in regulating Th1 cells, we studied the effects of Ezh2 inhibition in CD4(+) T cells using a mouse model of human AA. Conditionally deleting Ezh2 in mature T cells dramatically reduced the production of BM-destructive Th1 cells in vivo, decreased BM-infiltrating Th1 cells, and rescued mice from BM failure. Ezh2 inhibition resulted in significant decrease in the expression of Tbx21 and Stat4, which encode transcription factors T-bet and STAT4, respectively. Introduction of T-bet but not STAT4 into Ezh2-deficient T cells fully rescued their differentiation into Th1 cells mediating AA. Ezh2 bound to the Tbx21 promoter in Th1 cells and directly activated Tbx21 transcription. Unexpectedly, Ezh2 was also required to prevent proteasome-mediated degradation of T-bet protein in Th1 cells. Our results demonstrate that Ezh2 promotes the generation of BM-destructive Th1 cells through a mechanism of transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of T-bet. These results also highlight the therapeutic potential of Ezh2 inhibition in reducing AA and other autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The histone methyltransferase Ezh2 is a crucial epigenetic regulator of allogeneic T-cell responses mediating graft-versus-host disease.Blood. 2013 Dec 12;122(25):4119-28. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-505180. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24141370 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of NOTCH signaling ameliorates immune-mediated bone marrow failure of aplastic anemia.J Exp Med. 2013 Jul 1;210(7):1311-29. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112615. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23733784 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of cyclosporine A on the expression of T-bet, GATA-3, relevant signal transduction molecules, cytokine and Th1/Th2 balance in patients with chronic aplastic anemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Oct;18(5):1211-9. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21129263 Chinese.
-
[Expression of T-bet and its regulation on CD4(+) T cell polarization in aplastic anemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;19(2):546-9. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21518527 Review. Chinese.
-
New therapeutic approaches for protecting hematopoietic stem cells in aplastic anemia.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):34-43. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8449-0. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24203441 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling trajectories from aplastic anemia to hematologic malignancies: genetic and molecular insights.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 13;14:1365614. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1365614. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38544839 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 inhibition destabilizes Ezh2 protein in alloreactive T cells and reduces graft-versus-host disease in mice.Blood. 2017 May 18;129(20):2737-2748. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-735886. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28246193 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CD4 T-cell differentiation and inflammation by repressive histone methylation.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;93(3):245-52. doi: 10.1038/icb.2014.115. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25582341 Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming by miRNAs in the tumor microenvironment: Focused on immunometabolism.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 22;12:1042196. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1042196. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36483029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The histone methyltransferase EZH2 primes the early differentiation of follicular helper T cells during acute viral infection.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Mar;17(3):247-260. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0219-z. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 30842630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araki Y, Wang Z, Zang C, Wood WH, 3rd, Schones D, Cui K, Roh TY, Lhotsky B, Wersto RP, Peng W, Becker KG, Zhao K, Weng NP. Genome-wide analysis of histone methylation reveals chromatin state-based regulation of gene transcription and function of memory CD8+ T cells. Immunity. 2009;30:912–925. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bantignies F, Cavalli G. Cellular memory and dynamic regulation of polycomb group proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

