Liver x receptors stimulate lipogenesis in bovine mammary epithelial cell culture but do not appear to be involved in diet-induced milk fat depression in cows
- PMID: 24760520
- PMCID: PMC4002246
- DOI: 10.1002/phy2.266
Liver x receptors stimulate lipogenesis in bovine mammary epithelial cell culture but do not appear to be involved in diet-induced milk fat depression in cows
Abstract
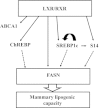
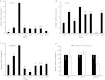
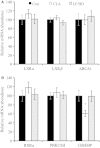
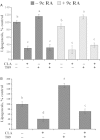
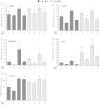
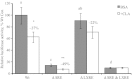
Abstract Milk fat synthesis of ruminants can be inhibited by intermediates of ruminal fatty acid biohydrogenation including trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). These biohydrogenation intermediates signal a coordinated downregulation of genes involved in mammary FA synthesis, transport, and esterification. We have previously reported decreased mammary expression of sterol response element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), SREBP1-activating proteins, and thyroid hormone-responsive spot 14 (S14) in the cow during diet-induced milk fat depression (MFD), and treatment with trans-10, cis-12 CLA. Liver x receptors (LXR) and retinoid x receptors (RXR) regulate lipogenesis and are known to bind polyunsaturated FA and LXR agonist increases lipid synthesis in mammary epithelial cell culture. The current studies investigated if biohydrogenation products of rumen origin inhibit mammary lipogenesis through LXR and/or RXR. Expression of LXRs was not different in lactating compared to nonlactating bovine mammary tissue, and expression of LXRs, RXRα, and selected LXR and RXR target genes was not changed in mammary tissue during diet-induced or CLA-induced MFD in the cow. In bovine mammary epithelial cell culture, LXR agonist stimulated lipogenesis and expression of LXRß, ATP-binding cassette 1 (ABCA1), SREBP1c, and S14, but LXR activation did not overcome CLA inhibition of lipogenesis and downregulation of LXRß, SREBP1c, and S14 expression. Lastly, expression of the LXR-regulated carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) was higher in lactating than nonlactating tissue and was decreased during CLA-induced MFD. We conclude that changes in mammary LXR expression in dairy cows are not involved in MFD and that trans-10, cis-12 CLA inhibition of lipogenesis and diet-induced MFD appears independent of direct LXR signaling.
Keywords: Carbohydrate‐responsive element‐binding protein; conjugated linoleic acid; lipogenesis; liver x receptor; milk fat depression; retinoid x receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SREBP1 and thyroid hormone responsive spot 14 (S14) are involved in the regulation of bovine mammary lipid synthesis during diet-induced milk fat depression and treatment with CLA.J Nutr. 2006 Oct;136(10):2468-74. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.10.2468. J Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16988111
-
Role of trans fatty acids in the nutritional regulation of mammary lipogenesis in ruminants.Animal. 2010 Jul;4(7):1140-66. doi: 10.1017/S1751731110000510. Animal. 2010. PMID: 22444614
-
Potential involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in the inhibition of mammary lipid synthesis during diet-induced milk fat depression.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Feb;108(2):2036-2044. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25575. Epub 2024 Nov 8. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 39521416 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrigenomics, rumen-derived bioactive fatty acids, and the regulation of milk fat synthesis.Annu Rev Nutr. 2011 Aug 21;31:299-319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.012809.104648. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21568706 Review.
-
Modifying milk fat composition of dairy cows to enhance fatty acids beneficial to human health.Lipids. 2004 Dec;39(12):1197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11745-004-1348-6. Lipids. 2004. PMID: 15736916 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutrigenomic Effect of Saturated and Unsaturated Long Chain Fatty Acids on Lipid-Related Genes in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells: What Is the Role of PPARγ?Vet Sci. 2019 Jun 11;6(2):54. doi: 10.3390/vetsci6020054. Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212682 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Liver X Receptor in Mastitis Therapy and Regulation of Milk Fat Synthesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2019 Mar;24(1):73-83. doi: 10.1007/s10911-018-9403-5. Epub 2018 Jul 31. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 30066175 Review.
-
Molecular characterization and homology modeling of liver X receptor in Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer: predicted functions in reproduction and lipid metabolism.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2019 Apr;45(2):523-538. doi: 10.1007/s10695-019-00617-6. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30806874
-
Malonyl/Acetyltransferase (MAT) Knockout Decreases Triacylglycerol and Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Contents in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells.Foods. 2022 Apr 29;11(9):1291. doi: 10.3390/foods11091291. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35564013 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X receptor-α activation enhances cholesterol secretion in lactating mammary epithelium.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):E1136-E1145. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00548.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30964702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balmer J. E., Blomhoff R. 2002. Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid. J. Lipid Res.; 43:1773-1808. - PubMed
-
- Bauman D. E., Davis C. L. 1974. 31-75.inIn: Larson B. L., Smith V. R. (eds.). Biosynthesis of milk fat. Lactation: a comprehensive treatise 2New York: Academic Press Inc.
-
- Bauman D. E., Griinari J. M. 2003. Nutritional regulation of milk fat synthesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr.; 23:203-227. - PubMed
-
- Bauman D. E., Perfield J. W., II, Harvatine K. J., Baumgard L. H. 2008. Regulation of fat synthesis by conjugated linoleic acid: lactation and the ruminant model. J. Nutr.; 138:403-409. - PubMed
-
- Bauman D. E., Harvatine K. J., Lock A. L. 2011. Nutrigenomics, rumen‐derived bioactive fatty acids, and the regulation of milk fat synthesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr.; 31:299-319. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

