Nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain causes disinhibition of the anterior cingulate cortex
- PMID: 24760836
- PMCID: PMC6608297
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3667-13.2014
Nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain causes disinhibition of the anterior cingulate cortex
Abstract
Neuropathic pain caused by peripheral nerve injury is a debilitating neurological condition of high clinical relevance. On the cellular level, the elevated pain sensitivity is induced by plasticity of neuronal function along the pain pathway. Changes in cortical areas involved in pain processing contribute to the development of neuropathic pain. Yet, it remains elusive which plasticity mechanisms occur in cortical circuits. We investigated the properties of neural networks in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), a brain region mediating affective responses to noxious stimuli. We performed multiple whole-cell recordings from neurons in layer 5 (L5) of the ACC of adult mice after chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve of the left hindpaw and observed a striking loss of connections between excitatory and inhibitory neurons in both directions. In contrast, no significant changes in synaptic efficacy in the remaining connected pairs were found. These changes were reflected on the network level by a decrease in the mEPSC and mIPSC frequency. Additionally, nerve injury resulted in a potentiation of the intrinsic excitability of pyramidal neurons, whereas the cellular properties of interneurons were unchanged. Our set of experimental parameters allowed constructing a neuronal network model of L5 in the ACC, revealing that the modification of inhibitory connectivity had the most profound effect on increased network activity. Thus, our combined experimental and modeling approach suggests that cortical disinhibition is a fundamental pathological modification associated with peripheral nerve damage. These changes at the cortical network level might therefore contribute to the neuropathic pain condition.
Keywords: anterior cingulate cortex; chronic pain; disinhibition; neuronal network; structural plasticity.
Figures

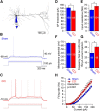
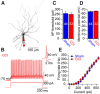
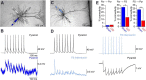

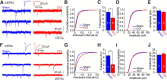

Similar articles
-
The Effect of Optogenetic Inhibition of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Neuropathic Pain Following Sciatic Nerve Injury.J Mol Neurosci. 2021 Mar;71(3):638-650. doi: 10.1007/s12031-020-01685-7. Epub 2020 Aug 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32808249
-
Chronic constriction injury induced long-term changes in spontaneous membrane-potential oscillations in anterior cingulate cortical neurons in vivo.Pain Physician. 2013 Sep-Oct;16(5):E577-89. Pain Physician. 2013. PMID: 24077208
-
Contralateral Projection of Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Mirror-Image Pain.J Neurosci. 2021 Dec 1;41(48):9988-10003. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0881-21.2021. Epub 2021 Oct 12. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34642215 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal and microglial mechanisms for neuropathic pain in the spinal dorsal horn and anterior cingulate cortex.J Neurochem. 2017 May;141(4):486-498. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14001. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28251660 Review.
-
Short-term synaptic plasticity in the nociceptive thalamic-anterior cingulate pathway.Mol Pain. 2009 Sep 4;5:51. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-51. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19732417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin Induces Analgesic Effects through MT2 Receptor-Mediated Neuroimmune Modulation in the Mice Anterior Cingulate Cortex.Research (Wash D C). 2024 Oct 8;7:0493. doi: 10.34133/research.0493. eCollection 2024. Research (Wash D C). 2024. PMID: 39381792 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of targeting the cingulate gyrus using high-intensity focused ultrasound on a cadaveric specimen: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Jul 15;8(3):CASE2459. doi: 10.3171/CASE2459. Print 2024 Jul 15. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 39008907 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Optogenetic Inhibition of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Neuropathic Pain Following Sciatic Nerve Injury.J Mol Neurosci. 2021 Mar;71(3):638-650. doi: 10.1007/s12031-020-01685-7. Epub 2020 Aug 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32808249
-
Up-regulation of microglial chemokine CXCL12 in anterior cingulate cortex mediates neuropathic pain in diabetic mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Jul;44(7):1337-1349. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-01046-7. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36697977 Free PMC article.
-
Homeostatic activity regulation as a mechanism underlying the effect of brain stimulation.Bioelectron Med. 2019 Sep 25;5:16. doi: 10.1186/s42234-019-0032-0. eCollection 2019. Bioelectron Med. 2019. PMID: 32232105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
