The role of Arp2/3 in growth cone actin dynamics and guidance is substrate dependent
- PMID: 24760849
- PMCID: PMC3996216
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0672-14.2014
The role of Arp2/3 in growth cone actin dynamics and guidance is substrate dependent
Abstract
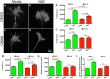
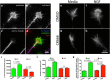
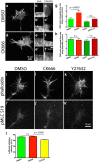
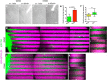
During development extrinsic guidance cues modulate the peripheral actin network in growth cones to direct axons to their targets. We wanted to understand the role of the actin nucleator Arp2/3 in growth cone actin dynamics and guidance. Since growth cones migrate in association with diverse adhesive substrates during development, we probed the hypothesis that the functional significance of Arp2/3 is substrate dependent. We report that Arp2/3 inhibition led to a reduction in the number of filopodia and growth cone F-actin content on laminin and L1. However, we found substrate-dependent differences in growth cone motility, actin retrograde flow, and guidance after Arp2/3 inhibition, suggesting that its role, and perhaps that of other actin binding proteins, in growth cone motility is substrate dependent.
Keywords: Arp2/3; L1 CAM; actin; growth cone; guidance; laminin.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Arp2/3 complex, UNC-115/abLIM, and UNC-34/Enabled regulate axon guidance and growth cone filopodia formation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Neural Dev. 2009 Oct 2;4:38. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-4-38. Neural Dev. 2009. PMID: 19799769 Free PMC article.
-
Local Arp2/3-dependent actin assembly modulates applied traction force during apCAM adhesion site maturation.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jan 1;28(1):98-110. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-04-0228. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 27852899 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule and Rac 1-dependent F-actin in growth cones.J Cell Sci. 2003 Sep 15;116(Pt 18):3739-48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00686. Epub 2003 Jul 30. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12890754
-
Actin dynamics in growth cone motility and navigation.J Neurochem. 2014 Apr;129(2):221-34. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12506. Epub 2013 Nov 17. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24164353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin-based growth cone motility and guidance.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Oct;84:4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28268126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Knockout of the Neuropsychiatric Risk Gene KCTD13 Causes Developmental Deficits in Human Cortical Neurons Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Feb;57(2):616-634. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01727-1. Epub 2019 Aug 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31402430
-
Grip and slip of L1-CAM on adhesive substrates direct growth cone haptotaxis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 13;115(11):2764-2769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711667115. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29483251 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer induced nociceptor aberrant growth and collateral sensory axonal branching.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 1;8(44):76606-76621. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20609. eCollection 2017 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29100335 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial roles of the Arp2/3 complex during mammalian corticogenesis.Development. 2016 Aug 1;143(15):2741-52. doi: 10.1242/dev.130542. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Development. 2016. PMID: 27385014 Free PMC article.
-
Astroglial exosome HepaCAM signaling and ApoE antagonization coordinates early postnatal cortical pyramidal neuronal axon growth and dendritic spine formation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 14:2023.02.14.528554. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.14.528554. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 24;14(1):5150. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40926-2. PMID: 36824898 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
