Infralimbic BDNF/TrkB enhancement of GluN2B currents facilitates extinction of a cocaine-conditioned place preference
- PMID: 24760865
- PMCID: PMC3996223
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4980-13.2014
Infralimbic BDNF/TrkB enhancement of GluN2B currents facilitates extinction of a cocaine-conditioned place preference
Abstract
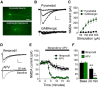
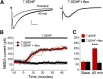
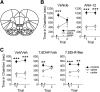
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates synaptic activity and behavioral flexibility, and reduction of BDNF strongly predicts psychiatric disorders and cognitive dysfunction. Restoration of BDNF-dependent activity could alleviate these impairments, but BDNF has limited clinical utility due to its pharmacokinetics. Here we demonstrate that activation of a primary BDNF target, the tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) receptor, enhances the amplitude and prolongs the decay kinetics of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) currents in male rat infralimbic prefrontal pyramidal neurons. Moreover, these effects were prevented and reversed by blockade of NMDARs containing the GluN2B subunit. Our results show that this signaling cascade bidirectionally regulates extinction of a cocaine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP), a task that requires behavioral flexibility. Blockade of infralimbic TrkB receptors or GluN2B-containing NMDARs disrupted consolidation of extinction of the CPP. In contrast, extinction was strengthened by potentiation of TrkB receptor activity with infralimbic infusions of BDNF or systemic injections of 7,8 dihydroxyflavone (7,8DHF), the newly synthesized TrkB receptor agonist. The 7,8DHF-induced enhancement of extinction was prevented by infralimbic infusions of a GluN2B-specific receptor antagonist, demonstrating that TrkB receptor activation enhances extinction of cocaine-CPP via GluN2B-containing NMDARs. Together, infralimbic TrkB receptor activation strengthens GluN2B-containing NMDAR currents to support extinction learning. TrkB receptor agonists would therefore be useful as pharmacological adjuncts for extinction-based therapies for treatment of psychiatric disorders associated with reduced BDNF activity.
Keywords: NR2B-containing NMDA receptor; TrkB receptor; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; extinction learning; medial prefrontal cortex; patch-clamp electrophysiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of accumbens BDNF and TrkB in cocaine-induced psychomotor sensitization, conditioned-place preference, and reinstatement in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Aug;199(2):169-82. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1164-1. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18551281
-
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Modulates Synaptic Plasticity in the Infralimbic Cortex via Trk-B Receptor Activation to Reduce Drug-Seeking in Male Rats.J Neurosci. 2024 Jun 5;44(23):e0107242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0107-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38719446 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a small-molecule TrkB agonist, on emotional learning.Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Feb;168(2):163-72. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10030326. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21123312 Free PMC article.
-
Fear extinction and BDNF: translating animal models of PTSD to the clinic.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Jul;11(5):503-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00801.x. Epub 2012 May 11. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22530815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of BDNF and GDNF in drug reward and relapse: a review.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010 Nov;35(2):157-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010. PMID: 19914287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted delivery of brain-derived neurotrophic factor for the treatment of blindness and deafness.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Apr 30;10:3245-67. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S77480. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25995632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of the Centromedial Amygdala Glutamatergic Synapses by the BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Aug;40(9):2269-77. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.76. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25786582 Free PMC article.
-
Fear extinction requires ASIC1a-dependent regulation of hippocampal-prefrontal correlates.Sci Adv. 2018 Oct 24;4(10):eaau3075. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau3075. eCollection 2018 Oct. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30417090 Free PMC article.
-
Rottlerin, BDNF, and the impairment of inhibitory avoidance memory.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Feb;238(2):421-439. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05690-x. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33146738
-
Adolescent social defeat alters N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor expression and impairs fear learning in adulthood.Behav Brain Res. 2016 May 1;304:51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26876136 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
