Evaluating melanoma drug response and therapeutic escape with quantitative proteomics
- PMID: 24760959
- PMCID: PMC4083119
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M113.037424
Evaluating melanoma drug response and therapeutic escape with quantitative proteomics
Abstract
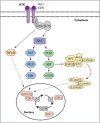
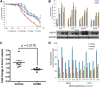
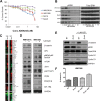
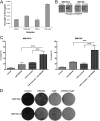
The evolution of cancer therapy into complex regimens with multiple drugs requires novel approaches for the development and evaluation of companion biomarkers. Liquid chromatography-multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry (LC-MRM) is a versatile platform for biomarker measurement. In this study, we describe the development and use of the LC-MRM platform to study the adaptive signaling responses of melanoma cells to inhibitors of HSP90 (XL888) and MEK (AZD6244). XL888 had good anti-tumor activity against NRAS mutant melanoma cell lines as well as BRAF mutant cells with acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors both in vitro and in vivo. LC-MRM analysis showed HSP90 inhibition to be associated with decreased expression of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases, modules in the PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, and the MAPK/CDK4 signaling axis in NRAS mutant melanoma cell lines and the inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling in BRAF mutant melanoma xenografts with acquired vemurafenib resistance. The LC-MRM approach targeting more than 80 cancer signaling proteins was highly sensitive and could be applied to fine needle aspirates from xenografts and clinical melanoma specimens (using 50 μg of total protein). We further showed MEK inhibition to be associated with signaling through the NFκB and WNT signaling pathways, as well as increased receptor tyrosine kinase expression and activation. Validation studies identified PDGF receptor β signaling as a potential escape mechanism from MEK inhibition, which could be overcome through combined use of AZD6244 and the PDGF receptor inhibitor, crenolanib. Together, our studies show LC-MRM to have unique value as a platform for the systems level understanding of the molecular mechanisms of drug response and therapeutic escape. This work provides the proof-of-principle for the future development of LC-MRM assays for monitoring drug responses in the clinic.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The HSP90 inhibitor XL888 overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance mediated through diverse mechanisms.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 May 1;18(9):2502-14. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2612. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22351686 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028973. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194965 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Wee1, AKT, and CDK4 underlies the efficacy of the HSP90 inhibitor XL888 in an in vivo model of NRAS-mutant melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Jun;12(6):901-12. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1003. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23538902 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of molecular alterations with immune response in melanoma.Cancer. 2017 Jun 1;123(S11):2130-2142. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30681. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28543700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in melanoma: targeting the MAPK pathway.Discov Med. 2015 Jun;19(107):455-61. Discov Med. 2015. PMID: 26175403 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted mass spectrometry-based assays enable multiplex quantification of receptor tyrosine kinase, MAP Kinase, and AKT signaling.Cell Rep Methods. 2021 Jul 26;1(3):100015. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100015. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Cell Rep Methods. 2021. PMID: 34671754 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Profiling of Protein Tyrosine Kinases in Human Cancer Cell Lines by Multiplexed Parallel Reaction Monitoring Assays.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Feb;15(2):682-91. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O115.056713. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26631510 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in PI3KR2-overexpressing colon cancer stem cells reduces tumor growth due to apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 8;8(31):50476-50488. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9919. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 28881576 Free PMC article.
-
Parsing interindividual drug variability: an emerging role for systems pharmacology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2015 Jul-Aug;7(4):221-41. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1302. Epub 2015 May 7. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25950758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
17-Aminogeldanamycin selectively diminishes IRE1α-XBP1s pathway activity and cooperatively induces apoptosis with MEK1/2 and BRAFV600E inhibitors in melanoma cells of different genetic subtypes.Apoptosis. 2019 Aug;24(7-8):596-611. doi: 10.1007/s10495-019-01542-y. Apoptosis. 2019. PMID: 30989459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chapman P. B., Hauschild A., Robert C., Haanen J. B., Ascierto P., Larkin J., Dummer R., Garbe C., Testori A., Maio M., Hogg D., Lorigan P., Lebbe C., Jouary T., Schadendorf D., Ribas A., O'Day S. J., Sosman J. A., Kirkwood J. M., Eggermont A. M., Dreno B., Nolop K., Li J., Nelson B., Hou J., Lee R. J., Flaherty K. T., McArthur G. A. (2011) Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 364, 2507–2516 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trunzer K., Pavlick A. C., Schuchter L., Gonzalez R., McArthur G. A., Hutson T. E., Moschos S. J., Flaherty K. T., Kim K. B., Weber J. S., Hersey P., Long G. V., Lawrence D., Ott P. A., Amaravadi R. K., Lewis K. D., Puzanov I., Lo R. S., Koehler A., Kockx M., Spleiss O., Schell-Steven A., Gilbert H. N., Cockey L., Bollag G., Lee R. J., Joe A. K., Sosman J. A., Ribas A. (2013) Pharmacodynamic effects and mechanisms of resistance to vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 31, 1767–1774 - PubMed
-
- Poulikakos P. I., Persaud Y., Janakiraman M., Kong X., Ng C., Moriceau G., Shi H., Atefi M., Titz B., Gabay M. T., Salton M., Dahlman K. B., Tadi M., Wargo J. A., Flaherty K. T., Kelley M. C., Misteli T., Chapman P. B., Sosman J. A., Graeber T. G., Ribas A., Lo R. S., Rosen N., Solit D. B. (2011) RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature 480, 387–390 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

