Lysophosphatidic acid stimulation of NHE3 exocytosis in polarized epithelial cells occurs with release from NHERF2 via ERK-PLC-PKCδ signaling
- PMID: 24760985
- PMCID: PMC4080180
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00045.2014
Lysophosphatidic acid stimulation of NHE3 exocytosis in polarized epithelial cells occurs with release from NHERF2 via ERK-PLC-PKCδ signaling
Abstract
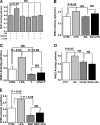
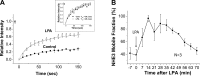
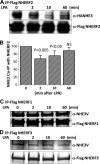
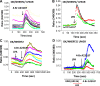
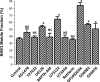
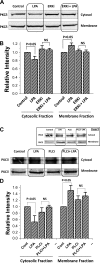
The Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 3 (NHE3) is a brush border (BB) Na(+)/H(+) antiporter that accounts for the majority of physiologic small intestinal and renal Na(+) absorption. It is regulated physiologically and in disease via changes in endocytosis/exocytosis. Paradoxically, NHE3 is fixed to the microvillar (MV) actin cytoskeleton and has little basal mobility. This fixation requires NHE3 binding to the multi-PDZ domain scaffold proteins Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF)1 and NHERF2 and to ezrin. Coordinated release of NHE3 from the MV cytoskeleton has been demonstrated during both stimulation and inhibition of NHE3. However, the signaling molecules involved in coordinating NHE3 trafficking and cytoskeletal association have not been identified. This question was addressed by studying lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) stimulation of NHE3 in polarized renal proximal tubule opossum kidney (OK) cells that occurs via apical LPA5 receptors and is NHERF2 dependent and mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), Rho/Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), and ERK. NHE3 activity was determined by BCECF/fluorometry and NHE3 microvillar mobility by FRAP/confocal microscopy using NHE3-EGFP. Apical LPA (3 μM)/LPA5R stimulated NHE3 activity, increased NHE3 mobility, and decreased the NHE3/NHERF2 association. The LPA stimulation of NHE3 was also PKCδ dependent. PKCδ was necessary for LPA stimulation of NHE3 mobility and NHE3/NHERF2 association. Moreover, the LPA-induced translocation to the membrane of PKCδ was both ERK and phospholipase C dependent with ERK acting upstream of PLC. We conclude that LPA stimulation of NHE3 exocytosis includes a signaling pathway that regulates fixation of NHE3 to the MV cytoskeleton. This involves a signaling module consisting of ERK-PLC-PKCδ, which dynamically and reversibly releases NHE3 from NHERF2 to contribute to the changes in NHE3 MV mobility.
Keywords: FRAP; NHE3; PDZ domain; microvillus; trafficking.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures





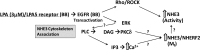
References
-
- Cha B, Kenworthy A, Murtazina R, Donowitz M. The lateral mobility of NHE3 on the apical membrane of renal epithelial OK cells is limited by the PDZ domain proteins NHERF1/2, but is dependent on an intact actin cytoskeleton as determined by FRAP. J Cell Sci 117: 3353–3365, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Cha B, Kim JH, Hut H, Hogema BM, Nadarja J, Zizak M, Cavet M, Lee-Kwon W, Lohmann SM, Smolenski A, Tse CM, Yun C, de Jonge HR, Donowitz M. cGMP inhibition of Na+/H+ antiporter 3 (NHE3) requires PDZ domain adapter NHERF2, a broad specificity protein kinase G-anchoring protein. J Biol Chem 280: 16642–16650, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Choi JW, Lim S, Oh YS, Kim EK, Kim SH, Kim YH, Heo K, Kim J, Kim JK, Yang YR, Ryu SH, Suh PG. Subtype-specific role of phospholipase C-beta in bradykinin and LPA signaling through differential binding of different PDZ scaffold proteins. Cell Signal 22: 1153–1161, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

