Inhibitory Effect of Acupuncture on Vibration-Induced Finger Flexion Reflex in Humans: Comparisons Among Radial, Median, and Ulnar Nerve Stimulation
- PMID: 24761176
- PMCID: PMC3746284
- DOI: 10.1089/acu.2012.0955
Inhibitory Effect of Acupuncture on Vibration-Induced Finger Flexion Reflex in Humans: Comparisons Among Radial, Median, and Ulnar Nerve Stimulation
Abstract
Background: Vibration-induced finger flexion reflex (VFR) is inhibited with acupuncture to TE 5 or LI 4 at the skin innervated by the radial nerve.
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine if acupoints in regions innervated by the radial nerve are specific to inhibit VFR.
Materials and methods: This experiment was performed using a crossover design with 3 acupuncture groups (needle insertion to the right LU 11, PC 9, or SI 1) and a control group (no needle treatment). Each acupoint was randomly needled on separate days. Ten healthy volunteers were recruited for this study. VFR was induced by applying vibration on the volar side of the right middle fingertip. An acupuncture needle was inserted in the acupoint and retained for 5 minutes. For the main outcome measure, maximum finger flexion force (MFFF) was measured during vibration and was compared among four groups.
Results: MFFFs in the acupuncture groups were significantly lower (p<0.05) than that in the control group. However, no significant difference was observed in MFFFs in the three intervention groups after acupuncture to LU 11, PC 9, and SI 1.
Conclusions: Acupuncture to the right LU 11, PC 9, or SI 1 point inhibited the ipsilateral VFR, which suggests that afferent inputs from the radial nerve with needle insertion were not specific, compared with those from the median and ulnar nerves to suppress neuronal activities in the VFR reflex circuits.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Flexion Reflex; Median Nerve; Radial Nerve; Stiff Muscles; Ulnar Nerve; Vibration.
Figures



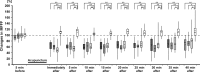
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of needle penetration on vibration-induced finger flexion reflex in humans.Acupunct Med. 2010 Jun;28(2):78-82. doi: 10.1136/aim.2009.001149. Epub 2010 May 10. Acupunct Med. 2010. PMID: 20458124 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of acupuncture at right Hoku point on the bilateral vibration-induced finger flexion reflex in man.Am J Chin Med. 1992;20(2):115-26. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X92000126. Am J Chin Med. 1992. PMID: 1519552 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of acupuncture at the Hoku point on vibration-induced finger flexion reflex in man: comparison between press needle technique, electroacupuncture, and in-situ technique.Am J Chin Med. 1995;23(3-4):313-8. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X95000377. Am J Chin Med. 1995. PMID: 8571928
-
Upper-extremity peripheral nerve injuries: a Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center literature review with comparison of the operative outcomes of 1837 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center median, radial, and ulnar nerve lesions.Neurosurgery. 2009 Oct;65(4 Suppl):A11-7. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000339130.90379.89. Neurosurgery. 2009. PMID: 19927055 Review.
-
Neural mechanisms of reflex inhibition of heart rate elicited by acupuncture-like stimulation in anesthetized rats.Auton Neurosci. 2010 Oct 28;157(1-2):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.03.021. Epub 2010 May 10. Auton Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20460195 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of a randomised acupuncture trial on functional neck/shoulder stiffness with two placebo controls.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jul 16;14:246. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-246. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25027157 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects on Acupuncturist Blinding: Different Diameters of Double-blind Acupuncture Needles.Altern Ther Health Med. 2021 Sep;27(5):62-66. Altern Ther Health Med. 2021. PMID: 33038081 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Stux G. Berman B. Pomeranz B. Basics of Acupuncture. Berlin, Heidelberg & New York: Springer-Verlag; 2003. Scientific basis of acupuncture; pp. 7–86.
-
- Helms MJ. Acupuncture Energetics. New York: Thieme; 1995. Treating musculoskeletal pain; pp. 457–520.
-
- Hecker UH. Steveling A. Peuker TE. Kastner J. Practice of Acupuncture. New York: Thieme; 2005. Pragmatic five-step concept for treating locomotor pain and headaches; pp. 421–435.
-
- Baldry EP. Acupuncture, Trigger Points and Musculoskeletal Pain. Brookline, MA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2005. Principles of trigger point acupuncture, The practical application of trigger point acupuncture; pp. 45–358.
-
- Barlas P. Ting SL. Chesterton LS. Jones PW. Sim J. Effects of intensity of electroacupuncture upon experimental pain in healthy human volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pain. 2006;122(1–2):81–89. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
