Repeatability of in vivo 3D lamina cribrosa microarchitecture using adaptive optics spectral domain optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 24761293
- PMCID: PMC3986004
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.5.001114
Repeatability of in vivo 3D lamina cribrosa microarchitecture using adaptive optics spectral domain optical coherence tomography
Abstract
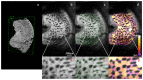
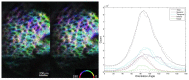
We demonstrate the repeatability of lamina cribrosa (LC) microarchitecture for in vivo 3D optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans of healthy, glaucoma suspects, and glaucomatous eyes. Eyes underwent two scans using a prototype adaptive optics spectral domain OCT (AO-SDOCT) device from which LC microarchitecture was semi-automatically segmented. LC segmentations were used to quantify pore and beam structure through several global microarchitecture parameters. Repeatability of LC microarchitecture was assessed qualitatively and quantitatively by calculating parameter imprecision. For all but one parameters (pore volume) measurement imprecision was <4.7% of the mean value, indicating good measurement reproducibility. Imprecision ranged between 27.3% and 54.5% of the population standard deviation for each parameter, while there was not a significant effect on imprecision due to disease status, indicating utility in testing for LC structural trends.
Keywords: (100.2000) Digital image processing; (110.4500) Optical coherence tomography; (170.1610) Clinical applications; (170.4470) Ophthalmology; (330.4460) Ophthalmic optics and devices.
Figures




Similar articles
-
In vivo three-dimensional characterization of the healthy human lamina cribrosa with adaptive optics spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Sep 16;55(10):6459-66. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-15177. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25228539 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of in-vivo OCT measured three-dimensional human lamina cribrosa microarchitecture.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):e95526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095526. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24747957 Free PMC article.
-
Automated lamina cribrosa microstructural segmentation in optical coherence tomography scans of healthy and glaucomatous eyes.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Oct 24;4(11):2596-608. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.002596. eCollection 2013. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 24298418 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of the Lamina Cribrosa using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography.J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2012 Sep-Dec;6(3):113-9. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1117. Epub 2012 Oct 16. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2012. PMID: 26997766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Swept-Source OCT for Evaluating the Lamina Cribrosa: A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.Ophthalmology. 2019 Sep;126(9):1315-1323. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.03.044. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Ophthalmology. 2019. PMID: 30953743 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional adaptive optics optical coherence tomography allows cellular scale reflectometry, polarimetry, and angiography in the living human eye.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Jan 31;15(2):1331-1354. doi: 10.1364/BOE.505395. eCollection 2024 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 38404344 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in optical coherence tomography.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015 Mar;26(2):110-5. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000133. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25594766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Future of Imaging in Detecting Glaucoma Progression.Ophthalmology. 2017 Dec;124(12S):S76-S82. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.10.011. Ophthalmology. 2017. PMID: 29157365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lamina Cribrosa Microstructure in Nonhuman Primates With Naturally Occurring Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thinning.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Sep 3;13(9):23. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.9.23. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39297808 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography and Glaucoma.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2021 Sep 15;7:693-726. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-100419-111350. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34242054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leung C. K. S., Lam S., Weinreb R. N., Liu S., Ye C., Liu L., He J., Lai G. W. K., Li T., Lam D. S., “Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: analysis of the retinal nerve fiber layer map for glaucoma detection,” Ophthalmology 117(9), 1684–1691 (2010).10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.01.026 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
