Repeatability of in vivo 3D lamina cribrosa microarchitecture using adaptive optics spectral domain optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 24761293
- PMCID: PMC3986004
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.5.001114
Repeatability of in vivo 3D lamina cribrosa microarchitecture using adaptive optics spectral domain optical coherence tomography
Abstract
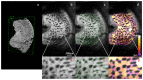
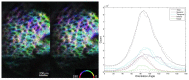
We demonstrate the repeatability of lamina cribrosa (LC) microarchitecture for in vivo 3D optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans of healthy, glaucoma suspects, and glaucomatous eyes. Eyes underwent two scans using a prototype adaptive optics spectral domain OCT (AO-SDOCT) device from which LC microarchitecture was semi-automatically segmented. LC segmentations were used to quantify pore and beam structure through several global microarchitecture parameters. Repeatability of LC microarchitecture was assessed qualitatively and quantitatively by calculating parameter imprecision. For all but one parameters (pore volume) measurement imprecision was <4.7% of the mean value, indicating good measurement reproducibility. Imprecision ranged between 27.3% and 54.5% of the population standard deviation for each parameter, while there was not a significant effect on imprecision due to disease status, indicating utility in testing for LC structural trends.
Keywords: (100.2000) Digital image processing; (110.4500) Optical coherence tomography; (170.1610) Clinical applications; (170.4470) Ophthalmology; (330.4460) Ophthalmic optics and devices.
Figures




References
-
- Leung C. K. S., Lam S., Weinreb R. N., Liu S., Ye C., Liu L., He J., Lai G. W. K., Li T., Lam D. S., “Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: analysis of the retinal nerve fiber layer map for glaucoma detection,” Ophthalmology 117(9), 1684–1691 (2010).10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.01.026 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
