Polyglutamine Disease Modeling: Epitope Based Screen for Homologous Recombination using CRISPR/Cas9 System
- PMID: 24761311
- PMCID: PMC3994193
- DOI: 10.1371/currents.hd.0242d2e7ad72225efa72f6964589369a
Polyglutamine Disease Modeling: Epitope Based Screen for Homologous Recombination using CRISPR/Cas9 System
Abstract
We have previously reported the genetic correction of Huntington's disease (HD) patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells using traditional homologous recombination (HR) approaches. To extend this work, we have adopted a CRISPR-based genome editing approach to improve the efficiency of recombination in order to generate allelic isogenic HD models in human cells. Incorporation of a rapid antibody-based screening approach to measure recombination provides a powerful method to determine relative efficiency of genome editing for modeling polyglutamine diseases or understanding factors that modulate CRISPR/Cas9 HR.
Figures
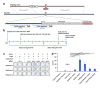
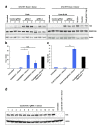
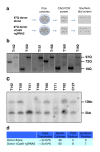

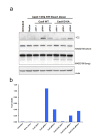
References
-
- Yang, L., Mali, P., Kim-Kiselak, C. & Church, G. CRISPR-Cas-Mediated Targeted Genome Editing in Human Cells. Methods Mol Biol 1114, 245-267, doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-761-7_16 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Bassett, A. R. & Liu, J. L. CRISPR/Cas9 and Genome Editing in Drosophila. Journal of genetics and genomics = Yi chuan xue bao 41, 7-19, doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2013.12.004 (2014). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

