Design and construction of an optical computed tomography scanner for polymer gel dosimetry application
- PMID: 24761377
- PMCID: PMC3994717
Design and construction of an optical computed tomography scanner for polymer gel dosimetry application
Abstract
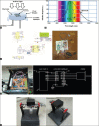
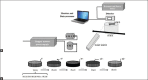
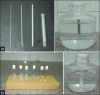
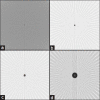
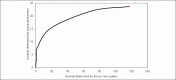
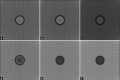
Polymer gel dosimeter is the only accurate three dimensional (3D) dosimeter that can measure the absorbed dose distribution in a perfect 3D setting. Gel dosimetry by using optical computed tomography (OCT) has been promoted by several researches. In the current study, we designed and constructed a prototype OCT system for gel dosimetry. First, the electrical system for optical scanning of the gel container using a Helium-Neon laser and a photocell was designed and constructed. Then, the mechanical part for two rotational and translational motions was designed and step motors were assembled to it. The data coming from photocell was grabbed by the home-built interface and sent to a personal computer. Data processing was carried out using MATLAB software. To calibrate the system and tune up the functionality of it, different objects was designed and scanned. Furthermore, the spatial and contrast resolution of the system was determined. The system was able to scan the gel dosimeter container with a diameter up to 11 cm inside the water phantom. The standard deviation of the pixels within water flask image was considered as the criteria for image uniformity. The uniformity of the system was about ±0.05%. The spatial resolution of the system was approximately 1 mm and contrast resolution was about 0.2%. Our primary results showed that this system is able to obtain two-dimensional, cross-sectional images from polymer gel samples.
Keywords: Optical computed tomography; polymer gel dosimetry; two-dimensional imaging system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validation of a Prototype Optical Computed Tomography System.J Med Signals Sens. 2015 Apr-Jun;5(2):123-30. J Med Signals Sens. 2015. PMID: 26120572 Free PMC article.
-
A prototype fan-beam optical CT scanner for 3D dosimetry.Med Phys. 2013 Jun;40(6):061712. doi: 10.1118/1.4805111. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23718591
-
Three-dimensional dose verification for intensity modulated radiation therapy using optical CT based polymer gel dosimetry.Med Phys. 2006 May;33(5):1412-9. doi: 10.1118/1.2188820. Med Phys. 2006. PMID: 16752577
-
Three-dimensional radiation dosimetry using polymer gel and solid radiochromic polymer: From basics to clinical applications.World J Radiol. 2017 Mar 28;9(3):112-125. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i3.112. World J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28396725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation dosimetry using polymer gels: methods and applications.Br J Radiol. 2000 Sep;73(873):919-29. doi: 10.1259/bjr.73.873.11064643. Br J Radiol. 2000. PMID: 11064643 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of a Prototype Optical Computed Tomography System.J Med Signals Sens. 2015 Apr-Jun;5(2):123-30. J Med Signals Sens. 2015. PMID: 26120572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jirasek A, Rudko D, Wells D. A prototype fan-beam optical CT scanner for polymer gel dosimetry. 5th International Conference on Radiotherapy Gel Dosimetry (DOSGEL 2008). Conference Series. J Phys. 2009;164:1–6.
-
- Oldham M, Siewerdsen JH, Shetty A, Jaffray DA. High resolution gel-dosimetry by optical-CT and MR scanning. Med Phys. 2001;28:1436–45. - PubMed
-
- Olding T, Holmes O, Schreiner LJ. Cone beam optical computed tomography for gel dosimetry I: Scanner characterization. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:2819–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

