Cloning, expression, purification and characterisation of Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 24761390
- PMCID: PMC3988593
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.127995
Cloning, expression, purification and characterisation of Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background: For the past 30 years, bacterial L-asparaginases have been used as therapeutic agents in the treatment of acute childhood lymphoblastic leukemia. It is found in a variety of organisms such as microbes, plants and mammals. Their intrinsic low-rate glutaminase activity, however, causes serious side-effects, including neurotoxicity, hepatitis, coagulopathy and other dysfunctions. Erwinia carotovora asparaginase shows decreased glutaminase activity, so it is believed to have fewer side-effects in leukemia therapy. Our aim was to clone, express, purify and characterize E. carotovora asparaginase.
Materials and methods: L-asparaginase from E. carotovora NCYC 1526 (ErA) was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3). The enzyme was purified to homogeneity by affinity chromatography. Various conditions were tested to maximize the production of recombinant asparaginase in E. coli.
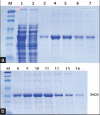
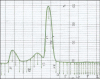
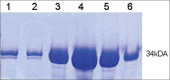
Results: A new L. asparaginase from E. carotovora NCYC 1526 (ErA) was successfully cloned, expressed and purified in E. coli BL21 (DE3). The specific activity of the enzyme was 430 IU/mg.
Conclusion: The results of the present work form the basis for a new engineered form of ErA for future therapeutic use, which could be extended with crystallographic studies.
Keywords: Characterization; ErA; Erwinia carotovora; Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3); L-asparaginase; cloning; purification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structural and functional insights into Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase.FEBS J. 2008 Sep;275(17):4306-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06574.x. Epub 2008 Jul 21. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18647344
-
Cloning, expression and characterisation of Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase.J Biotechnol. 2005 Oct 10;119(4):309-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.04.016. J Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 15951039
-
[Purification and properties of recombinant Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase expressed in E.coli cells].Biomed Khim. 2003 Sep-Oct;49(5):502-7. Biomed Khim. 2003. PMID: 16119104 Russian.
-
Bacterial l-asparaginases for cancer therapy: Current knowledge and future perspectives.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):19271-19279. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28563. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30993718 Review.
-
[Bacterial recombinant L-asparaginases: properties, structure and anti-proliferative activity].Biomed Khim. 2015 May-Jun;61(3):312-24. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20156103312. Biomed Khim. 2015. PMID: 26215408 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
L-Asparaginase from Penicillium sizovae Produced by a Recombinant Komagataella phaffii Strain.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 14;15(6):746. doi: 10.3390/ph15060746. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745665 Free PMC article.
-
L-Asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora: insights about its stability and activity.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1313-1316. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4459-2. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30446961
-
Highly Active Thermophilic L-Asparaginase from Melioribacter roseus Represents a Novel Large Group of Type II Bacterial L-Asparaginases from Chlorobi-Ignavibacteriae-Bacteroidetes Clade.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 20;22(24):13632. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413632. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948436 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural evaluation of the antileukaemic enzyme L-asparaginase II expressed at low temperature by different Escherichia coli strains.Biotechnol Lett. 2020 Nov;42(11):2333-2344. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-02955-5. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Biotechnol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32638188
-
Expression and Functional Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Recombinant L.Asparaginase.Protein J. 2018 Oct;37(5):461-471. doi: 10.1007/s10930-018-9789-3. Protein J. 2018. PMID: 30097831
References
-
- Campbell HA, Mashburn LT, Boyse EA, Old LJ. Two L-asparaginases from Escherichia coli B. Their separation, purification, and antitumor activity. Biochemistry. 1967;6:721–30. - PubMed
-
- Duval M, Suciu S, Ferster A, Rialland X, Nelken B, Lutz P, et al. Comparison of Escherichia coli-asparaginase with Erwinia-asparaginase in the treatment of childhood lymphoid malignancies: Results of a randomized European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Children's Leukemia Group phase 3 trial. Blood. 2002;99:2734–9. - PubMed
-
- Gökbuget N, Hoelzer D. Treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006;1:133–41. - PubMed
-
- Verma N, Kumar K, Kaur G, Anand S. L-asparaginase: A promising chemotherapeutic agent. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2007;27:45–62. - PubMed
-
- Lee SM, Wroble MH, Ross JT. L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora. An improved recovery and purification process using affinity chromatography. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1989;22:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

