The effect of erythropoietin to pulmonary injury and mast cells secondary to acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 24761770
- PMCID: PMC4004514
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-267
The effect of erythropoietin to pulmonary injury and mast cells secondary to acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Background: Acute pancreatitis is a life-threatening necroinflammatory disease that is characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome and acute lung injury even in its very first days. Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone considered as an antiapoptotic and cytoprotective with observed receptors of anti-inflammatory effect on organs apart from the liver and the kidneys. In this study, the effects of EPO on pulmonary mast cells and on secondary injury caused by acute pancreatitis are investigated.
Methods: Twenty one Wistar Albino rats were divided into three groups--sham, control, and EPO groups-with 7 rats per group. Pancreatitis was induced by administering 4.5% sodium taurocholate into the pancreatic duct. A 1000 U/kg/day dosage (three times) of EPO was administered to the EPO group. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, amylase, and troponin I in the serum were studied; and lung, kidney, brain, and heart tissues were examined histopathologically.
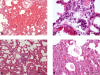
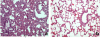
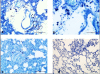
Results: There were no histopathological changes in the other organ tissues except for the lung tissue. Compared to the control group, the EPO group showed significantly reduced alveolar hemorrhage, septal neutrophil infiltration, lung wall thickness score, and mast cell count in the lung tissue.
Conclusions: Administration of EPO reduces the mast cell count and lung wall thickness, and it reduces the alveolar hemorrhage and septal infiltration induced by acute pancreatitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of erythropoietin against acute lung injury in a rat model of acute necrotizing pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Dec 14;13(46):6172-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i46.6172. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 18069756 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin: a possible cytoprotective cytokine in acute necrotizing pancreatitis.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009;16(4):530-7. doi: 10.1007/s00534-009-0082-x. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009. PMID: 19333535
-
Erythropoietin attenuates renal and pulmonary injury in polymicrobial induced-sepsis through EPO-R, VEGF and VEGF-R2 modulation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;82:606-13. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.045. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27470403
-
Protective effects of erythropoietin on endotoxin-related organ injury in rats.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Oct;33(5):680-686. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1180-1. Epub 2013 Oct 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24142720
-
[Characterisation of the protective role of erythropoetin in a murine model of acute lung injury].Rev Mal Respir. 2020 Mar;37(3):193-196. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Rev Mal Respir. 2020. PMID: 32146057 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Erythropoietin and its derivatives: from tissue protection to immune regulation.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Feb 3;11(2):79. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2276-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32015330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Perspective on Erythropoietin as a Potential Adjuvant Therapy for Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Patients with COVID-19.Arch Med Res. 2020 Oct;51(7):631-635. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Arch Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32863034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin in Optic Neuropathies: Current Future Strategies for Optic Nerve Protection and Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 27;23(13):7143. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137143. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new organ preservation solution for static cold storage of the liver. Amniotic fluid.Acta Cir Bras. 2019 Apr 29;34(4):e201900402. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020190040000002. Acta Cir Bras. 2019. PMID: 31038582 Free PMC article.
-
Coping with hypoxemia: Could erythropoietin (EPO) be an adjuvant treatment of COVID-19?Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020 Aug;279:103476. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2020.103476. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32522574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, Lau HY, Huang J, Puneet P, Chevali L. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2005;5(2–3):132–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

