Identification of breast cancer patients with a high risk of developing brain metastases: a single-institutional retrospective analysis
- PMID: 24761771
- PMCID: PMC4006960
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-289
Identification of breast cancer patients with a high risk of developing brain metastases: a single-institutional retrospective analysis
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to identify breast cancer patients with a high risk of developing brain metastases who may benefit from pre-emptive medical intervention.
Methods: Medical records of 352 breast cancer patients with local or locoregional disease at diagnosis were retrospectively analysed. The brain metastasis-free survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and patient groups were compared using the log rank test. The simultaneous relationship of multiple prognostic factors was assessed using Cox's proportional hazard regression analysis. The Fisher exact test was used to test the difference of proportions for statistical significance.
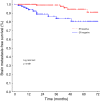
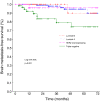
Results: On univariate analysis, statistically highly significant unfavourable risk factors for the brain metastasis-free survival were negative ER status, negative PR status, and triple negative tumor subtype. Young age at diagnosis (≤35 years) and advanced disease stage were not statistically significant (p = 0.10). On multivariate analysis, the only independent significant factor was the ER status (negative ER status; hazard radio (95% confidence interval), 5.1 (1.8-14.6); p = 0.003). In the subgroup of 168 patients with a minimum follow-up of 24 months, 49 patients developed extracranial metastases as first metastatic event. Of those, 7 of 15 (46.6%) with a negative ER status developed brain metastases compared to 5 of 34 (14.7%) with a positive ER status (Fisher exact test, p = 0.03). The median time interval (minimum-maximum) between the diagnosis of extracranial and brain metastases was 7.5 months (1-30 months).
Conclusions: Breast cancer patients with extracranial metastasis and negative ER status exhibited an almost 50% risk of developing brain metastasis during their course of disease. Future studies are highly desired to evaluate the efficacy of pre-emptive medical intervention such as prophylactic treatment or diagnostic screening for high risk breast cancer patients.
Figures
References
-
- Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study Cancer. 1983;52(12):2349–2354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous