Macrophagic and microglial responses after focal traumatic brain injury in the female rat
- PMID: 24761998
- PMCID: PMC4022366
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-82
Macrophagic and microglial responses after focal traumatic brain injury in the female rat
Abstract
Background: After central nervous system injury, inflammatory macrophages (M1) predominate over anti-inflammatory macrophages (M2). The temporal profile of M1/M2 phenotypes in macrophages and microglia after traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats is unknown. We subjected female rats to severe controlled cortical impact (CCI) and examined the postinjury M1/M2 time course in their brains.
Methods: The motor cortex (2.5 mm left laterally and 1.0 mm anteriorly from the bregma) of anesthetized female Wistar rats (ages 8 to 10 weeks; N = 72) underwent histologically moderate to severe CCI with a 5-mm impactor tip. Separate cohorts of rats had their brains dissociated into cells for flow cytometry, perfusion-fixed for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and ex vivo magnetic resonance imaging or flash-frozen for RNA and protein analysis. For each analytical method used, separate postinjury times were included for 24 hours; 3 or 5 days; or 1, 2, 4 or 8 weeks.
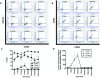
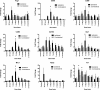
Results: By IHC, we found that the macrophagic and microglial responses peaked at 5 to 7 days post-TBI with characteristics of mixed populations of M1 and M2 phenotypes. Upon flow cytometry examination of immunological cells isolated from brain tissue, we observed that peak M2-associated staining occurred at 5 days post-TBI. Chemokine analysis by multiplex assay showed statistically significant increases in macrophage inflammatory protein 1α and keratinocyte chemoattractant/growth-related oncogene on the ipsilateral side within the first 24 hours after injury relative to controls and to the contralateral side. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis demonstrated expression of both M1- and M2-associated markers, which peaked at 5 days post-TBI.
Conclusions: The responses of macrophagic and microglial cells to histologically severe CCI in the female rat are maximal between days 3 and 7 postinjury. The response to injury is a mixture of M1 and M2 phenotypes.
Figures




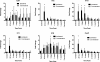

References
-
- Faul M, Xu L, Wald MM, Coronado VG. Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths 2002–2006. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control; 2010. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/pdf/blue_book.pdf; (accessed 15 April 2014)
-
- Bell RS, Vo AH, Neal CJ, Tigno J, Roberts R, Mossop C, Dunne JR, Armonda RA. Military traumatic brain and spinal column injury: a 5-year study of the impact blast and other military grade weaponry on the central nervous system. J Trauma. 2009;66(4 Suppl):S104–S111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

