Inhibitors - cellular aspects and novel approaches for tolerance
- PMID: 24762281
- PMCID: PMC4205104
- DOI: 10.1111/hae.12407
Inhibitors - cellular aspects and novel approaches for tolerance
Abstract
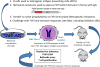
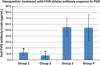
The immune response against therapeutic clotting factors VIII and IX (FVIII and FIX) is a major adverse event that can effectively thwart their effectiveness in correcting bleeding disorders. Thus, a significant number of haemophilia patients form antibodies, called inhibitors, which neutralize the procoagulant functions of therapeutic cofactors FVIII (haemophilia A) or FIX (haemophilia B). Understanding the cellular and molecular aspects of inhibitor formation is critical to designing tolerogenic therapies for clinical use. This review will focus on the basis of the immune response to FVIII, in particular, and will discuss emerging efforts to not only reduce immunogenicity but also to prevent and/or reverse inhibitor formation.
Keywords: factor VIII; gene therapy; haemophilia; immunoglobulin fusions; regulatory T cells.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Playfair JH. A cellular basis for auto-immunity. Essays Fundam Immunol. 1973:44–56. - PubMed
-
- Singh NJ, Schwartz RH. Primer: mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2:44–52. - PubMed
-
- Aledort LM, Evatt BL, Lusher JM, Brown-stein AP. HIV and hemophilia. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:607–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

