Looking beneath the surface to determine what makes DNA damage deleterious
- PMID: 24762292
- PMCID: PMC4149920
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.03.018
Looking beneath the surface to determine what makes DNA damage deleterious
Abstract
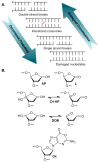
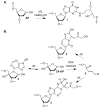
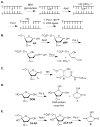
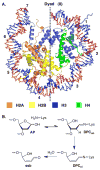
Apurinic/apyrimidinic and oxidized abasic sites are chemically reactive DNA lesions that are produced by a variety of damaging agents. The effects of these molecules that lack a Watson-Crick base on polymerase enzymes are well documented. More recently, multiple consequences of the electrophilic nature of abasic lesions have been revealed. Members of this family of DNA lesions have been shown to inactivate repair enzymes and undergo spontaneous transformation into more deleterious forms of damage. Abasic site reactivity provides insight into the chemical basis for the cytotoxicity of DNA damaging agents that produce them and are valuable examples of how looking beneath the surface of seemingly simple molecules can reveal biologically relevant chemical complexity.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Galm U, Hager MH, Van Lanen SG, Ju J, Thorson JS, Shen B. Antitumor antibiotics: Bleomycin, enediynes, and mitomycin. Chem Rev. 2005;105:739–758. - PubMed
-
- Pitié M, Pratviel G. Activation of DNA carbon hydrogen bonds by metal complexes. Chem Rev. 2010;110:1018–1059. - PubMed
-
- Delaney JC, Essigmann JM. Assays for determining lesion bypass efficiency and mutagenicity of site-specific DNA lesions in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 2006;408:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Bjelland S, Seeberg E. Mutagenicity, toxicity and repair of DNA base damage induced by oxidation. Mutation Res. 2003;531:37–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

