A quality control mechanism coordinates meiotic prophase events to promote crossover assurance
- PMID: 24762417
- PMCID: PMC3998905
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004291
A quality control mechanism coordinates meiotic prophase events to promote crossover assurance
Abstract
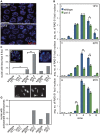
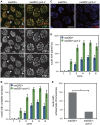
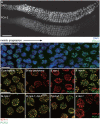
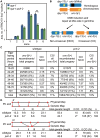
Meiotic chromosome segregation relies on homologous chromosomes being linked by at least one crossover, the obligate crossover. Homolog pairing, synapsis and meiosis specific DNA repair mechanisms are required for crossovers but how they are coordinated to promote the obligate crossover is not well understood. PCH-2 is a highly conserved meiotic AAA+-ATPase that has been assigned a variety of functions; whether these functions reflect its conserved role has been difficult to determine. We show that PCH-2 restrains pairing, synapsis and recombination in C. elegans. Loss of pch-2 results in the acceleration of synapsis and homolog-dependent meiotic DNA repair, producing a subtle increase in meiotic defects, and suppresses pairing, synapsis and recombination defects in some mutant backgrounds. Some defects in pch-2 mutants can be suppressed by incubation at lower temperature and these defects increase in frequency in wildtype worms grown at higher temperature, suggesting that PCH-2 introduces a kinetic barrier to the formation of intermediates that support pairing, synapsis or crossover recombination. We hypothesize that this kinetic barrier contributes to quality control during meiotic prophase. Consistent with this possibility, defects in pch-2 mutants become more severe when another quality control mechanism, germline apoptosis, is abrogated or meiotic DNA repair is mildly disrupted. PCH-2 is expressed in germline nuclei immediately preceding the onset of stable homolog pairing and synapsis. Once chromosomes are synapsed, PCH-2 localizes to the SC and is removed in late pachytene, prior to SC disassembly, correlating with when homolog-dependent DNA repair mechanisms predominate in the germline. Indeed, loss of pch-2 results in premature loss of homolog access. Altogether, our data indicate that PCH-2 coordinates pairing, synapsis and recombination to promote crossover assurance. Specifically, we propose that the conserved function of PCH-2 is to destabilize pairing and/or recombination intermediates to slow their progression and ensure their fidelity during meiotic prophase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The conserved AAA ATPase PCH-2 distributes its regulation of meiotic prophase events through multiple meiotic HORMADs in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2023 Apr 14;19(4):e1010708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010708. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37058535 Free PMC article.
-
PCH-2 collaborates with CMT-1 to proofread meiotic homolog interactions.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jul 30;16(7):e1008904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008904. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32730253 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved ATPase PCH-2 controls the number and distribution of crossovers by antagonizing their formation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Elife. 2025 Feb 18;13:RP102409. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102409. Elife. 2025. PMID: 39964851 Free PMC article.
-
Homologue pairing, recombination and segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genome Dyn. 2009;5:43-55. doi: 10.1159/000166618. Genome Dyn. 2009. PMID: 18948706 Review.
-
Targeting Polo-like kinase in space and time during C. elegans meiosis.Cell Cycle. 2021 Aug;20(16):1519-1526. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1953232. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34266376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis PCH2 Mediates Meiotic Chromosome Remodeling and Maturation of Crossovers.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 16;11(7):e1005372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005372. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26182244 Free PMC article.
-
The CSN/COP9 signalosome regulates synaptonemal complex assembly during meiotic prophase I of Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2014 Nov 6;10(11):e1004757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004757. eCollection 2014 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25375142 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved AAA ATPase PCH-2 distributes its regulation of meiotic prophase events through multiple meiotic HORMADs in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2023 Apr 14;19(4):e1010708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010708. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37058535 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Pch2 localization determinants reveals a nucleolar-independent role in the meiotic recombination checkpoint.Chromosoma. 2019 Sep;128(3):297-316. doi: 10.1007/s00412-019-00696-7. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Chromosoma. 2019. PMID: 30859296
-
Meiosis.WormBook. 2017 May 4;2017:1-43. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.178.1. WormBook. 2017. PMID: 26694509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baudat F, de Massy B (2007) Regulating double-stranded DNA break repair towards crossover or non-crossover during mammalian meiosis. Chromosome Res 15: 565–577. - PubMed
-
- Borner GV, Kleckner N, Hunter N (2004) Crossover/noncrossover differentiation, synaptonemal complex formation, and regulatory surveillance at the leptotene/zygotene transition of meiosis. Cell 117: 29–45. - PubMed
-
- Bishop DK, Zickler D (2004) Early decision; meiotic crossover interference prior to stable strand exchange and synapsis. Cell 117: 9–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

