Nutrient-driven O-GlcNAc cycling - think globally but act locally
- PMID: 24762810
- PMCID: PMC4004970
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.113233
Nutrient-driven O-GlcNAc cycling - think globally but act locally
Abstract
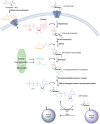
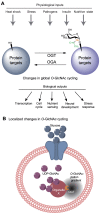
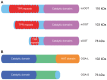
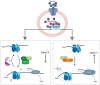
Proper cellular functioning requires that cellular machinery behave in a spatiotemporally regulated manner in response to global changes in nutrient availability. Mounting evidence suggests that one way this is achieved is through the establishment of physically defined gradients of O-GlcNAcylation (O-linked addition of N-acetylglucosamine to serine and threonine residues) and O-GlcNAc turnover. Because O-GlcNAcylation levels are dependent on the nutrient-responsive hexosamine signaling pathway, this modification is uniquely poised to inform upon the nutritive state of an organism. The enzymes responsible for O-GlcNAc addition and removal are encoded by a single pair of genes: both the O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and the O-GlcNAcase (OGA, also known as MGEA5) genes are alternatively spliced, producing protein variants that are targeted to discrete cellular locations where they must selectively recognize hundreds of protein substrates. Recent reports suggest that in addition to their catalytic functions, OGT and OGA use their multifunctional domains to anchor O-GlcNAc cycling to discrete intracellular sites, thus allowing them to establish gradients of deacetylase, kinase and phosphatase signaling activities. The localized signaling gradients established by targeted O-GlcNAc cycling influence many important cellular processes, including lipid droplet remodeling, mitochondrial functioning, epigenetic control of gene expression and proteostasis. As such, the tethering of the enzymes of O-GlcNAc cycling appears to play a role in ensuring proper spatiotemporal responses to global alterations in nutrient supply.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Lipid droplets; Metabolism; Mitochondria; Nuclear pores; O-GlcNAc; O-GlcNAcylation; Post-translational modification; Signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Adams R. R., Maiato H., Earnshaw W. C., Carmena M. (2001). Essential roles of Drosophila inner centromere protein (INCENP) and aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J. Cell Biol. 153, 865–880 10.1083/jcb.153.4.865 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

