Knowledge-based fragment binding prediction
- PMID: 24762971
- PMCID: PMC3998881
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003589
Knowledge-based fragment binding prediction
Abstract
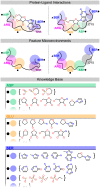
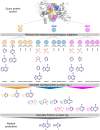
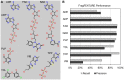
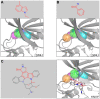
Target-based drug discovery must assess many drug-like compounds for potential activity. Focusing on low-molecular-weight compounds (fragments) can dramatically reduce the chemical search space. However, approaches for determining protein-fragment interactions have limitations. Experimental assays are time-consuming, expensive, and not always applicable. At the same time, computational approaches using physics-based methods have limited accuracy. With increasing high-resolution structural data for protein-ligand complexes, there is now an opportunity for data-driven approaches to fragment binding prediction. We present FragFEATURE, a machine learning approach to predict small molecule fragments preferred by a target protein structure. We first create a knowledge base of protein structural environments annotated with the small molecule substructures they bind. These substructures have low-molecular weight and serve as a proxy for fragments. FragFEATURE then compares the structural environments within a target protein to those in the knowledge base to retrieve statistically preferred fragments. It merges information across diverse ligands with shared substructures to generate predictions. Our results demonstrate FragFEATURE's ability to rediscover fragments corresponding to the ligand bound with 74% precision and 82% recall on average. For many protein targets, it identifies high scoring fragments that are substructures of known inhibitors. FragFEATURE thus predicts fragments that can serve as inputs to fragment-based drug design or serve as refinement criteria for creating target-specific compound libraries for experimental or computational screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Pammolli F, Magazzini L, Riccaboni M (2011) The productivity crisis in pharmaceutical R&D. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10: 428–438. - PubMed
-
- Scannell JW, Blanckley A, Boldon H, Warrington B (2012) Diagnosing the decline in pharmaceutical R&D efficiency. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11: 191–200. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins AL, Groom CR (2002) The druggable genome. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1: 727–730. - PubMed
-
- Bolton E, Wang Y, Thiessen PA, SH B (2008) PubChem: Integrated Platform of Small Molecules and Biological Activities. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

