Almost all antipsychotics result in weight gain: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24763306
- PMCID: PMC3998960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094112
Almost all antipsychotics result in weight gain: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Antipsychotics (AP) induce weight gain. However, reviews and meta-analyses generally are restricted to second generation antipsychotics (SGA) and do not stratify for duration of AP use. It is hypothesised that patients gain more weight if duration of AP use is longer.
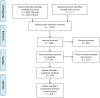
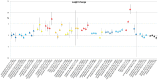
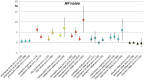
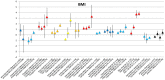
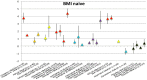
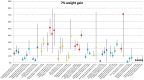
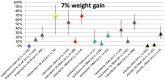
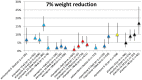
Method: A meta-analysis was conducted of clinical trials of AP that reported weight change. Outcome measures were body weight change, change in BMI and clinically relevant weight change (7% weight gain or loss). Duration of AP-use was stratified as follows: ≤6 weeks, 6-16 weeks, 16-38 weeks and >38 weeks. Forest plots stratified by AP as well as by duration of use were generated and results were summarised in figures.
Results: 307 articles met inclusion criteria. The majority were AP switch studies. Almost all AP showed a degree of weight gain after prolonged use, except for amisulpride, aripiprazole and ziprasidone, for which prolonged exposure resulted in negligible weight change. The level of weight gain per AP varied from discrete to severe. Contrary to expectations, switch of AP did not result in weight loss for amisulpride, aripiprazole or ziprasidone. In AP-naive patients, weight gain was much more pronounced for all AP.
Conclusion: Given prolonged exposure, virtually all AP are associated with weight gain. The rational of switching AP to achieve weight reduction may be overrated. In AP-naive patients, weight gain is more pronounced.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Henderson DC (2008) Managing weight gain and metabolic issues in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 69: e04. - PubMed
-
- Huxley R, Mendis S, Zheleznyakov E, Reddy S, Chan J (2010) Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular risk–a review of the literature. Eur J Clin Nutr 64: 16–22. - PubMed
-
- Meltzer HY (2001) Putting metabolic side effects into perspective: risks versus benefits of atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 62 Suppl 27: 35–39 discussion 40-31. - PubMed
-
- Newcomer JW, Haupt DW (2006) The metabolic effects of antipsychotic medications. Can J Psychiatry 51: 480–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

