The prognostic significance of early treatment response in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: results of the international study Relapsed AML 2001/01
- PMID: 24763401
- PMCID: PMC4562536
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2014.104182
The prognostic significance of early treatment response in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: results of the international study Relapsed AML 2001/01
Abstract
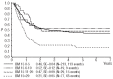
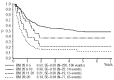
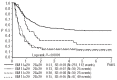
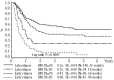
The prognostic significance of early response to treatment has not been reported in relapsed pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. In order to identify an early and easily applicable prognostic factor allowing subsequent treatment modifications, we assessed leukemic blast counts in the bone marrow by morphology on days 15 and 28 after first reinduction in 338 patients of the international Relapsed-AML2001/01 trial. Both day 15 and day 28 status was classified as good (≤20% leukemic blasts) in 77% of patients. The correlation between day 15 and 28 blast percentages was significant, but not strong (Spearman correlation coefficient = 0.49, P<0.001). Survival probability decreased in a stepwise fashion along with rising blast counts at day 28. Patients with bone marrow blast counts at this time-point of ≤5%, 6-10%, 11-20% and >20% had 4-year probabilities of survival of 52%±3% versus 36%±10% versus 21%±9% versus 14%±4%, respectively, P<0.0001; this trend was not seen for day 15 results. Multivariate analysis showed that early treatment response at day 28 had the strongest prognostic significance, superseding even time to relapse (< or ≥12 months). In conclusion, an early response to treatment, measured on day 28, is a strong and independent prognostic factor potentially useful for treatment stratification in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. This study was registered with ISRCTN code: 94206677.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
References
-
- Goemans BF, Tamminga RY, Corbijn CM, Hahlen K, Kaspers GJ. Outcome for children with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia in the Netherlands following initial treatment between 1980 and 1998: survival after chemotherapy only? Haematologica 2008;93(9):1418–20. - PubMed
-
- Gorman MF, Ji L, Ko RH, Barnette P, Bostrom B, Hutchinson R, et al. Outcome for children treated for relapsed or refractory acute myelogenous leukemia (rAML): a Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia (TACL) Consortium study. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010;55(3):421–9. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamsson J, Clausen N, Gustafsson G, Hovi L, Jonmundsson G, Zeller B, et al. Improved outcome after relapse in children with acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2007;136(2):229–36. - PubMed
-
- Aladjidi N, Auvrignon A, Leblanc T, Perel Y, Benard A, Bordigoni P, et al. Outcome in children with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia after initial treatment with the French Leucemie Aique Myeloide Enfant (LAME) 89/91 protocol of the French Society of Pediatric Hematology and Immunology. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(23): 4377–85. - PubMed
-
- Rubnitz JE, Razzouk BI, Lensing S, Pounds S, Pui CH, Ribeiro RC. Prognostic factors and outcome of recurrence in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 2007; 109(1):157–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

