Synthesis of IL-6 by hepatocytes is a normal response to common hepatic stimuli
- PMID: 24763697
- PMCID: PMC3999098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096053
Synthesis of IL-6 by hepatocytes is a normal response to common hepatic stimuli
Erratum in
-
Correction: Synthesis of IL-6 by Hepatocytes Is a Normal Response to Common Hepatic Stimuli.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 23;14(10):e0224498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224498. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31644563 Free PMC article.
Abstract
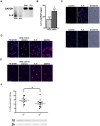
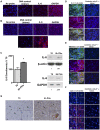
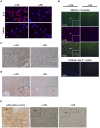
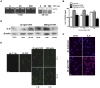
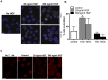
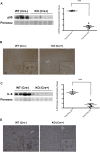
Exogenous interleukin 6 (IL-6), synthesized at the initiation of the acute phase response, is considered responsible for signaling hepatocytes to produce acute phase proteins. It is widely posited that IL-6 is either delivered to the liver in an endocrine fashion from immune cells at the site of injury, or alternatively, in a paracrine manner by hepatic immune cells within the liver. A recent publication showed there was a muted IL-6 response in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-injured mice when nuclear NFκB was specifically inactivated in the hepatocytes. This indicates hepatocellular signaling is also involved in regulating the acute phase production of IL-6. Herein, we present extensive in vitro and in vivo evidence that normal hepatocytes are directly induced to synthesize IL-6 mRNAs and protein by challenge with LPS, a bacterial hepatotoxin, and by HGF, an important regulator of hepatic homeostasis. As the IL-6 receptor is found on the hepatocyte, these results reveal that induction of the acute phase response can be regulated in an autocrine as well as endocrine/paracrine fashion. Further, herein we provide data indicating that following partial hepatectomy (PHx), HGF differentially regulates IL-6 production in hepatocytes (induces) versus immune cells (suppresses), signifying disparate regulation of the cell sources involved in IL-6 production is a biologically relevant mechanism that has previously been overlooked. These findings have wide ranging ramifications regarding how we currently interpret a variety of in vivo and in vitro biological models involving elements of IL-6 signaling and the hepatic acute phase response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Taub R (2004) Liver regeneration: from myth to mechanism. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 5: 836–847. - PubMed
-
- Gauldie J, Richards C, Baumann H (1992) IL6 and the acute phase reaction. Research in Immunology 143: 755–759. - PubMed
-
- Selzner N, Selzner M, Odermatt B, Tian Y, Van Rooijen N, et al. (2003) ICAM-1 triggers liver regeneration through leukocyte recruitment and Kupffer cell-dependent release of TNF-alpha/IL-6 in mice. Gastroenterology 124: 692–700. - PubMed
-
- Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, DeAngelis RA, Ciliberto G, Furth EE, et al. (1996) Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science 274: 1379–1383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

