Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation
- PMID: 24764505
- PMCID: PMC3834507
- DOI: 10.1186/1939-8433-5-5
Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation
Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic heavy metal which harms human health. In Japan, a major source of human Cd-intake is rice grains and contamination of paddy soils by Cd and accumulation of Cd in rice grains are the serious agricultural issues. There also exist Cd contamination of rice and its toxicity in several populations in countries including China and Thailand. Understanding the Cd transport mechanisms in rice can be a basis for regulating rice Cd transport and accumulation by molecular engineering and marker-assisted breeding. Recently, a number of studies have revealed the behavior of Cd in rice, genetic diversity of Cd accumulation, quantitative trait loci controlling Cd accumulation and transporter molecules regulating Cd accumulation and distribution in rice. In this article, we summarize recent advances in the field and discuss perspectives to reduce grain Cd contents.
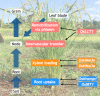
Figures

References
-
- Abe T, Taguchi-Shiobara F, Kojima Y, Ebitani T, Kuramata M, Yamamoto T, Yano M, Ishikawa S. Detection of a QTL for accumulating Cd in rice that enables efficient Cd phytoextraction from soil. Breeding Sci. 2011;5:43–51. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.61.43. - DOI
-
- Arao T, Ae N. Genotypic variations in cadmium levels of rice grain. Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2003;5:473–479. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2003.10410035. - DOI
-
- Arao T, Ae N, Sugiyama M, Takahashi M. Genotypic differences in cadmium uptake and distribution in soybeans. Plant Soil. 2003;5:247–253. doi: 10.1023/A:1023079819086. - DOI
-
- Asami T, Kubota M, Orikasa K. Distribution of different fractions of cadmium, zinc, lead, and copper in unpolluted and polluted soils. Water Air Soil Poll. 1995;5:187–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00477351. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

