2-(4,5-Di-chloro-2-nitro-phen-yl)-4-meth-oxy-3-methyl-9-phenyl-sulfon-yl-9H-carbazole
- PMID: 24764917
- PMCID: PMC3998356
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814001342
2-(4,5-Di-chloro-2-nitro-phen-yl)-4-meth-oxy-3-methyl-9-phenyl-sulfon-yl-9H-carbazole
Abstract
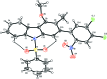
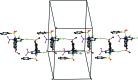
In the title compound, C26H18Cl2N2O5S, the carbazole ring system is essentially planar with a maximum deviation of 0.0498 (16) Å for the N atom. The carbazole ring system is almost orthogonal to the phenyl-sulfonyl and di-chloro-substituted nitro-phenyl rings, making dihedral angles of 84.23 (7) and 85.46 (12)°, respectively. The mol-ecular structure features intra-molecular C-H⋯O inter-actions, which generate two S(6) ring motifs. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by C-Cl⋯O halogen bonds [3.016 (3) Å, 166.63 (5)°], which generate infinite C(8) chains running parallel to [010].
Figures
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin. Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bassindale, A. (1984). The Third Dimension in Organic Chemistry, ch. 1, p. 11. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
